Live at 10 am Eastern/9 am Central time, and Streaming 24-7 Thereafter:
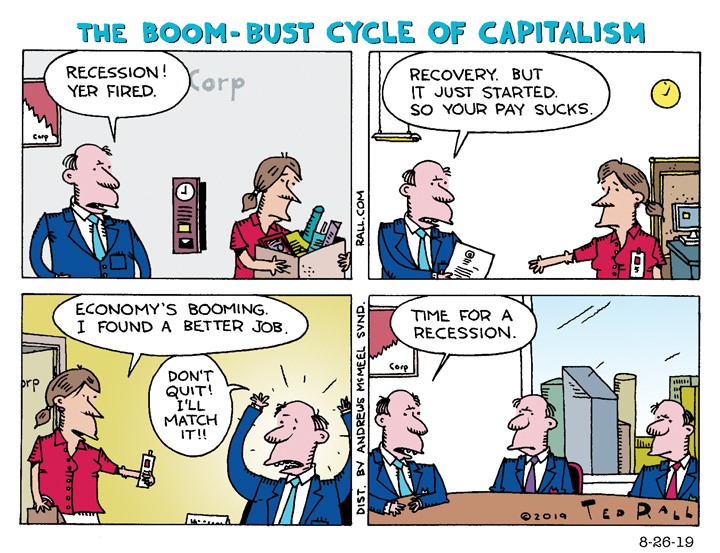
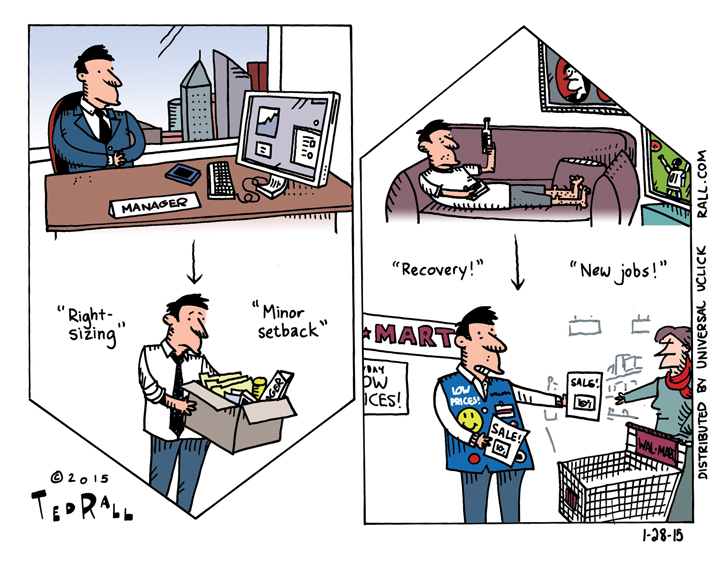
Historically, Bloomberg Economics has used a recession probability model that incorporates factors like housing permits, consumer sentiment, corporate profit outlooks, and Treasury yield gaps. It doesn’t always work. For example, in October 2022, they projected a 100% chance of a U.S. recession by October 2023, driven by aggressive Federal Reserve rate hikes, tightening financial conditions, and persistent inflation.
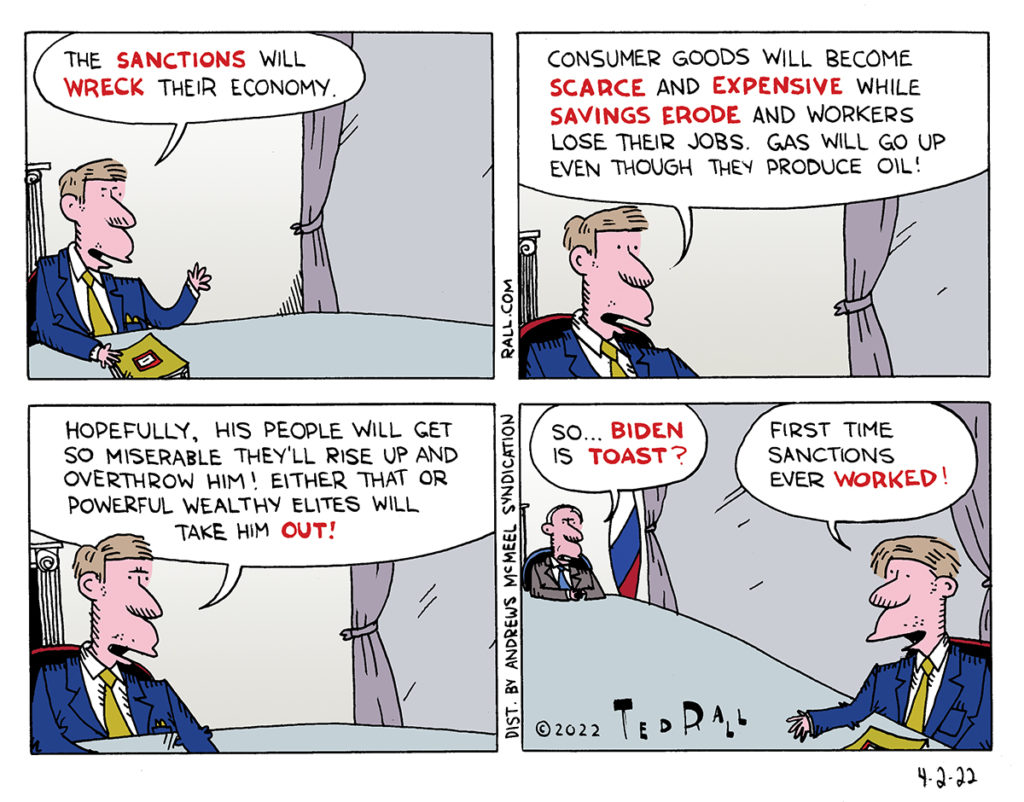
Here we go again. Consumer confidence fell this month by the most since August 2021 on concerns about the outlook for the broader economy, Bloomberg notes. Many consumers think we’ll see a recession later this year. That pessimism has more than half of consumers delaying major life plans due to uncertainty over the economy and the consequences of Trump’s tariff threats. Of those, about a third said they were putting off buying a home while one in six have postponed education plans—and one in eight have pushed back retirement.
On today’s episode of “The TMI Show,” Ted Rall and Manila Chan discuss the prospects for the economy with finance expert Aquiles Larrea.