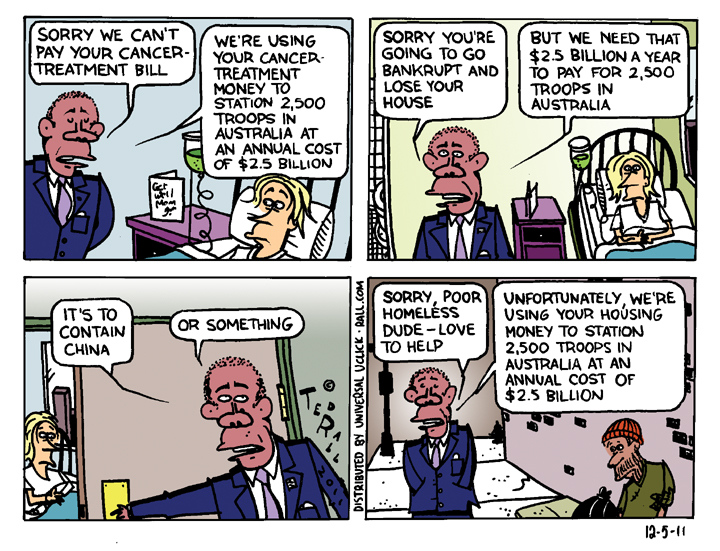
Obama announced that the U.S. will station 2,500 U.S. troops in northern Australia.
SYNDICATED COLUMN: American Dogs Count More Than Afghan People
Helicopter Shootdown Story Unmasks Bigoted Media
New York Times war correspondent Dexter Filkins couldn’t help liking the young American soldiers with whom he was embedded in U.S.-occupied Iraq. Recognizing that, Filkins tried to maintain some professional distance. “There wasn’t any point in sentimentalizing the kids; they were trained killers, after all. They could hit a guy at five hundred yards or cut his throat from ear-to-ear. They had faith, they did what they were told and they killed people,” he wrote in his book of war vignettes, “The Forever War.”
Alas, he was all but alone.
All wars demand contempt for The Other. But the leaders of a country waging a war of naked, unprovoked aggression are forced to rely on an even higher level of enemy dehumanization than average in order to maintain political support for the sacrifices they require. Your nation’s dead soldiers are glorious heroes fallen to protect hearth and home. Their dead soldiers are criminals and monsters. Their civilians are insects, unworthy of notice. So it is. So it always shall be in the endless battle over hearts and minds.
Even by these grotesque, inhuman rhetorical standards, the ten-year occupation of Afghanistan has been notable for the hyperbole relied upon by America’s compliant media as well as its brazen inconsistency.
U.S. and NATO officials overseeing the occupation of Afghanistan liken their mission to those of peacekeepers—they’re there to help. “Protecting the people is the mission,” reads the first line of the International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) Commander’s Counterinsurgency Guidance statement. “The conflict will be won by persuading the population, not by destroying the enemy. ISAF will succeed when the [Karzai government] earns the support of the people.”
Of course, actions speak louder than words. Since 2001 ISAF has been doing precious little protecting of anything other than America’s geopolitical interests, using Afghanistan as a staging ground for thousands of drone attacks across the border in Pakistan. Protecting Afghanistan civilians has actually been a low ISAF priority, to say the least. They’ve been bombing civilians indiscriminately, then lying about it, sometimes paying off bereaved family members with token sums of blood money.
The verbiage deployed by American officials, dutifully transcribed by journo-stenographers at official press briefings, sends nearly as loud a message as a laser-guided Hellfire missile slamming into a wedding party: Afghan lives mean nothing.
The life of an American dog—literally, as we’ll see below—counts more than that of an Afghan man or woman.
In the worst single-day loss of life for U.S. forces in Afghanistan, Taliban fighters shot down a Chinook CH-47 transport helicopter in eastern Wardak province with a rocket-propelled grenade on August 6th.
(I lifted that “worst single-day loss of life” phrase from numerous press accounts. The implication is obvious—the U.S. isn’t accustomed to taking losses. But tens of thousands of Afghans, possibly hundreds of thousands, have been killed in the war that began in 2001.)
Western media’s attitude toward the Afghans they are supposedly trying to “assist” was as plain as the headlines. “U.S. Troops, SEALs Killed in Afghanistan Copter Crash,” reported Time magazine. (SEALS are U.S. Navy commandos.) “31 Killed in Afghanistan Chopper Crash,” said the ABC television network. “31 Dead in Afghanistan Helicopter Crash,” shouted Canada’s National Post. (The number was later revised to 30.)
Eight Afghan government commandos died too. But dead Afghans don’t rate a headline—even when they’re working for your country’s puppet regime. As far as the American press is concerned, only 30 people—i.e., Americans—died.
An initial Associated Press wire service report noted that the dead included “22 SEALs, three Air Force air controllers, seven Afghan Army troops, a dog and his handler, and a civilian interpreter, plus the helicopter crew.”
The dog. They mentioned the dog.
And the dog’s handler.
After 9/11 American pundits debated the question: Why do they [radical Muslims] hate us [Americans] so much? This is why. It is official Pentagon policy not to count Afghan or Iraqi or Pakistani or Libyan or Yemeni or Somali dead, civilian or “enemy.” But “our” guys are sacred. We even count our dogs.
Lest you think that I’m exaggerating, that this was merely another example of a reporters larding his account with excessive detail, consider this maudlin missive by Michael Daly of the New York Daily News, one of the biggest newspapers in the United States:
“Among the SEALs were a dog handler and a dog that would remind outsiders of Cujo [a rabies-infected beast in one of Stephen King’s horror novels], but held a special place in the hearts of the squadron,” wrote Daly. “SEALs have a soft spot for their dogs, perhaps partly because a canine’s keen senses can alert them to danger and give them a critical edge. A dog also allows resolutely reticent warriors to express a little affection; you can pet a pooch, if not another SEAL.”
Get a grip, Mike. Lots of people like dogs.
“Many of the SEALs have a dog stateside,” continueth Daly. “To take one on a mission may be like bringing along something of home.”
Or maybe they just come in handy for Abu Ghraib-style interrogations.
Daly tortures and twists his cheesy prose into the kind of savage propaganda that prolongs a war the U.S. can’t win, that is killing Afghans and Americans for no reason, that most Americans prefer not to think about. Soon a group of elite commandos—members of Team Six, the same outfit that assassinated Osama bin Laden—become helpless victims of the all-seeing, all-powerful Taliban of Death. In Daly’s bizarre world, it is the Afghan resistance forces and their 1980s-vintage weapons that have all the advantages.
Note the infantile use of the phrase “bad guys.”
“The bad guys knew when the Chinook helicopter swooped down into an Afghan valley that it would have to rise once those aboard were done. All the Taliban needed to do was wait on a mountainside. The Chinook rose with a SEAL contingent that likely could have held off thousands of the enemy on the ground. The SEALs could do nothing in the air against an insurgent with a rocket.”
Helpless! One could almost forget whose country these Americans were in.
Or what they were in Wardak to do.
Early reports had the dead Navy SEALs on a noble “rescue mission” to “assist” beleaguered Army Rangers trapped under “insurgent” fire. Actually, Team Six was on an assassination assignment.
“The American commandos who died when their helicopter crashed in eastern Afghanistan were targeting a Taliban commander directly responsible for attacks on U.S. troops,” CNN television reported on August 7th. “Targeting” is mediaspeak for “killing.” According to some accounts they had just shot eight Talibs in a house in the village of Jaw-e-Mekh Zareen in the Tangi Valley. Hard to imagine, but U.S. soldiers used to try to capture enemy soldiers before killing them.
Within hours newspaper websites, radio and television outlets were choked with profiles of the dead assassins—er, heroes.
The AP described a dead SEAL from North Carolina as “physically slight but ever ready to take on a challenge.”
NBC News informed viewers that a SEAL from Connecticut had been “an accomplished mountaineer, skier, pilot and triathlete and wanted to return to graduate school and become an astronaut.”
What of the Afghans killed by those SEALs? What of their hopes and dreams? Americans will never know.
Two words kept coming up:
Poignant.
Tragedy (and tragic).
The usage was strange, outside of normal context, and revealing.
“Of the 30 Americans killed, 22 were members of an elite Navy SEAL team, something particularly poignant given it was Navy SEALS who succeeded so dramatically in the raid that killed Osama bin Laden,” said Renee Montaigne of National Public Radio, a center-right outlet that frequently draws fire from the far right for being too liberal.
Ironic, perhaps. But hardly poignant. Soldiers die by the sword. Ask them. They’ll tell you.
Even men of the cloth wallowed in the bloodthirsty militarism that has obsessed Americans since the September 11th attacks. Catholic News Service quoted Archbishop Timothy P. Broglio, who called the Chinook downing a “reminder of the terrible tragedy of war and its toll on all people.”
“No person of good will is left unmoved by this loss,” said the archbishop.
The Taliban, their supporters, and not a few random Afghans, may perhaps disagree.
This is a war, after all. Is it too much to ask the media to acknowledge the simple fact that some citizens of a nation under military occupation often choose to resist? That Americans might take up arms if things were the other way around, with Afghan occupation forces bombing and killing and torturing willy-nilly? That one side’s “insurgents” and “guerillas” are another’s patriots and freedom fighters?
Don’t news consumers have the right to hear from the “other” side of the story? Or must we continue the childish pretense that the Taliban are all women-hating fanatics incapable of rational thought while the men (and dog) who died on that Chinook in Wardak were all benevolent and pure of heart?
During America’s war in Vietnam reporters derided the “five o’clock follies,” daily press briefings that increasingly focused on body counts. Evening news broadcasts featured business-report-style graphics of the North and South Vietnamese flags; indeed, they immediately followed the stock market summary. “The Dow Jones Industrial Average was down 16 points in light trading,” Walter Cronkite would intone. “And in Vietnam today, 8 Americans were killed, 18 South Vietnamese, 43 Vietcong.”
Like the color-coded “threat assessment levels” issued by the Department of Homeland Security after 2001, the body counts became a national joke.
In many ways America’s next major conflict, the 1991 Gulf War, was a political reaction to the Vietnam experience. Conscription had been replaced by a professional army composed of de facto mercenaries recruited from the underclass. Overkill supplanted the war for hearts and minds that defined the late-Vietnam counterinsurgency strategy. And reporters who had enjoyed near total freedom in the 1960s were frozen out. Only a few trusted journos were allowed to travel with American forces in Kuwait and Iraq. They relied on the Pentagon to transmit their stories back home; one wire service reporter got back home to find that the military had blocked every single account he had filed.
Citing the five o’clock follies of Vietnam and declaring themselves incapable of counting civilian or enemy casualties, U.S. military officials said they would no longer bother to try. (Covertly, the bureaucracy continued to try to gather such data for internal use.)
Meanwhile, media organizations made excuses for not doing their jobs.
The UK Guardian, actually one of the better (i.e. not as bad) Western media outlets, summarized the mainstream view in August 2010: “While we are pretty good at providing detailed statistical breakdowns of coalition military casualties (and by we, I mean the media as a whole), we’ve not so good at providing any kind of breakdown of Afghan civilian casualties…Obviously, collecting accurate statistics in one of the most dangerous countries in the world is difficult. But the paucity of reliable data on this means that one of the key measures of the war has been missing from almost all reporting. You’ve noticed it too—asking us why we publish military deaths but not civilian casualties.”
No doubt, war zones are dangerous. According to Freedom Forum, 63 reporters lost their lives in Vietnam between 1955 and 1973—yet they strived to bring the war home to homes in the United States and other countries. And they didn’t just report military deaths.
There’s something more than a little twisted about media accounts that portray a helicopter shootdown as a “tragedy.”
A baby dies in a fire—that’s a tragedy. A young person struck down by some disease—that’s also a tragedy. Soldiers killed in war? Depending on your point of view, it can be sad. It can be unfortunate. It can suck. But it’s not tragic.
Alternately: If the United States’ losses in Afghanistan are “tragedies,” so are the Taliban’s. They can’t have it both ways.
“Tragedy Devastates Special Warfare Community,” blared a headline in USA Today. You’d almost have to laugh at the over-the-top cheesiness, the self-evident schmaltz, the crass appeal to vacuous emotionalism, in such ridiculous linguistic contortions. That is, if it didn’t describe something truly tragic—the death and mayhem that accompanies a pointless and illegal war.
On August 10th the U.S. military reported that they had killed the exact Talib who fired the RPG that brought down the Chinook. “Military officials said they tracked the insurgents after the attack, but wouldn’t clarify how they knew they had killed the man who had fired the fatal shot,” reported The Wall Street Journal.
“The conflict will be won by persuading the population, not by destroying the enemy.” But destroying the enemy is more fun.
(Ted Rall is the author of “The Anti-American Manifesto.” His website is tedrall.com.)
COPYRIGHT 2011 TED RALL
SYNDICATED COLUMN: Teddy Roosevelt Saw This Coming
The Decline and Fall of an American Icon
Why did our political system become so corrupt and unresponsive? How did we end up with such a rigid, Old European-style class system—in which you can’t get ahead unless you were born that way? America: What Went Wrong?, a 1992 paperback by Donald L. Barlett and James B. Steele, went a long way toward answering those questions.
It may be, however, that America was doomed long before then.
The historian Edmund Morris recently published the final entry of a magisterial trilogy about the life of Theodore Roosevelt. Though frequently listed among the greatest American politicians today, TR was an “accidental president” who ascended to power thanks to the murder of William McKinley. His blustery and impolitic style—his supporters called it speaking truth to power—would never have allowed him to win a presidential election.
Roosevelt sussed out the perils of unregulated capitalism early on. “The great corporations which we have grown to speak of rather loosely as trusts are the creatures of the State, and the State not only has the right to control them wherever need of such control is shown but it is in duty bound to control them,” he said in 1901.
No president since Nixon has followed TR’s advice. The result of unbridled corporate corruption is disparity of wealth worse than much of the Third World, and 20 percent unemployment.
Morris’ book Colonel Roosevelt addresses TR’s life after leaving the presidency in 1909: his 1912 run as on the independent Bull Moose ticket, his disastrous expedition through the Amazon, and finally the decline of this legendary dynamo after the start of World War I reordered the international landscape and doomed him to political irrelevance: a career bookended by assassins’ bullets.
Few presidents are as revered by both the left and the right. Liberals love TR for his record as an environmentalist and trust-buster. Conservatives like his unapologetic imperialism: the American empire as we know it began with Roosevelt.
Although it describes events that took place a century ago, this new biography shines light on many of the systemic ills that afflict the United States today.
On the domestic front it is brutally disheartening to read that even a figure as historically transcendent and contemporaneously popular as Theodore Roosevelt found it impossible to break the lock of the two major parties on the political process. As schoolchildren learn, the Bull Moose Party marks the apex of third party attempts in presidential politics. In 1912 it was an empty farce.
Along with their allied press barons, the Republican and Democratic Party machines blocked the charismatic (albeit longwinded) ex-Rough Rider every step of the way, rendering Roosevelt’s third-party defeat as much of a foregone conclusion as Nader’s.
During the Bull Moose run Roosevelt was shot at close range as he arrived for a campaign appearance in Milwaukee. The bullet, slowed by the printed text of the 50-page speech folded over in his jacket pocket, had nevertheless “pinked” the former president.
Morris’ description of TR’s grace under fire inspires awe: “Don’t hurt him. Bring him here,” Roosevelt shouted to men restraining his would-be assassin as he hoisted himself to his feet.
“Let’s go the hospital,” urged an aide.
“You get me to that speech,” Roosevelt replied, Morris says, “with a savage rasp to his voice.”
“[The bullet wound] was a ragged, dime-sized hole, bleeding slowly, about an inch below and to the right of his right nipple. The bullet was nowhere to be seen or palpated. The whole right side of his body had turned black,” Morris writes.
TR took the podium. “It takes more than that to kill a bull moose,” he said, going on to speak for an hour and fifteen minutes.
We have lost so much. Contrast TR’s courageous performance after being shot to our so-called “leaders.” On 9/11 George W. Bush abandoned Washington, fleeing into internal exile, hopscotching the nation like a coward before slinking back to the capital half a day later.
Roosevelt spent his last years hurling scathing critiques of Woodrow Wilson’s reluctance to enter World War I on the side of Britain and France. Nearly 100 years ago, however, the bellicose Roosevelt harbored no proto-neocon-like delusions about American exceptionalism—the nauseating combination of high-blown rhetoric and gutter-rat real-world actions that characterizes foreign policy of the United States and sparks outrage around the globe.
“He scoffed at the hypocrisy of Wilson’s grand-sounding phrase ‘self-determination for all peoples’ [in Wilson’s Fourteen Points], noting that the President was in no hurry to grant liberty to Haiti or Santo Domingo.” Both were under U.S. military occupation.
Were such self-awareness in greater supply in the U.S. today, we might not be fighting wars of aggression on three fronts at the same time we’re lecturing other countries about sovereignty and human rights.
Roosevelt’s martial spirit was his blind spot.
Unlike most Americans today, he had served valiantly. His bravery was unquestioned. One of his greatest disappointments was Wilson’s refusal to allow him to fight in the Great War.
Despite his experience in battle TR shared with today’s armchair “support our troops” “U-S-A” warriors an excess of willingness to send others to face shells and poison gas—without fully internalizing the consequences.
Despite being sidelined, Roosevelt pushed his sons to enlist and get to the fighting. Then his son Quentin, a pilot, got shot down. “Quentin’s mother and I are very glad that he got to the Front and had a chance to render some service to his country, and to show the stuff there was in him before his fate befell him,” he told the press.
But the cold reality of Quentin’s permanent absence marked the beginning of the end of a man known for his vigor. “The old side of him is gone, the old exuberance, the boy in him has died,” a friend noted the day after he learned of his son’s death. “I am not what I was,” TR confessed to his sister.
Two years later Roosevelt was dead, a victim of the American militarism he extolled and symbolized.
(Ted Rall is the author of “The Anti-American Manifesto.” His website is tedrall.com.)
COPYRIGHT 2011 TED RALL
SYNDICATED COLUMN: Thrifty Families and Other Lies
Like Their Government, Americans Live on Debt
his State of the Union address President Obama repeated this ancient canard: “We have to confront the fact that our government spends more than it takes in,” he said. “That is not sustainable. Every day, families sacrifice to live within their means. They deserve a government that does the same.”
Republicans have used this “families balance their budgets, so should government” line for years. Now Democrats are doing it too. Everyone is jumping aboard the pseudo-austerity bandwagon. (Why pseudo? Neither party really wants to balance the federal budget because it can only be done by bringing home the troops, shrinking the Pentagon by 90 percent, ending corporate welfare, and soaking the rich—i.e. major campaign donors—with higher taxes.)
The family budget talking point is a fascinating meme that reflects a rarely considered national blind spot. As with other cases of mass denial (we think we’re generous do-gooders around the world, foreigners see us for the crazy mean torturers we also are), we give ourselves more credit than we deserve.
We Americans value thrift and personal responsibility. We believe we should live within our means. These cultural ideals stem from our Puritan history.
But we don’t live up to our ideals. Not even close.
Americans are up to the ears in debt.
Four out of five individuals have at least one credit card. The average family has an outstanding balance of $10,700. It spends 21 percent of its monthly income to pay interest on that balance.
The average American family has assets: It owns a house worth $160,000. But it owes $95,000 to the bank. As the housing market continues to crash, equity shrinks.
Our average family’s savings are virtually nonexistent: $3,800 in the bank, no retirement account whatsoever (for half of families, average retirement savings $35,000 for the other half), no mutual funds, no stocks, no bonds.
The claim that American families live within their means is a joke.
To be fair, it’s not entirely their fault. The typical American family only earns $43,000. It’s hard to buy much of anything, much less the house that embodies the American Dream, with that. And it’s impossible to save.
So they/we borrow.
As grim as a life of indebted servitude may seem, imagine what the American economy would look like if families really did live within their means, spending no more than they earned. No debt. No credit.
Markets for big-ticket items—homes, automobiles, major appliances—would crash and burn. Countless businesses would go under.
According to the National Association of Realtors 23 percent of homebuyers paid cash in January. That’s more than ever before but that still leaves at least 77 percent relying on mortgage financing. (Why “at least”? Most “cash” transactions include money borrowed from banks and credit unions.) Take 77 percent of purchasers out of the buy side of the equation and million-dollar homes would be worth five figures.
Pop! Credit is the biggest bubble of all.
If credit went away, most Americans’ biggest asset would vanish. Everyone would be “under water” to their lenders. The burbs would soon look like Afghanistan.
The same goes for cars: At least 88 percent of buyers take out a loan.
What would happen if these buyers had to save actual cash money before they could hit the showroom? They wouldn’t buy a car. Air would get cleaner but the economic collapse that began in 2008, which has put one out of five Americans out of work, would accelerate dramatically.
Two-thirds of the U.S. economy directly relies on consumer spending. People can only purchase goods and services using one of three sources: income, savings or credit. As we’ve seen, the average American family doesn’t have savings. Its income has been falling since 1968.
That leaves credit. If consumer credit vanished, the corporato-capitalist system currently prevailing in the U.S. would deteriorate from its current, merely unsustainable form into total chaos. Without credit cards and other loans citizens would seethe, trapped between the mutually irreconcilable forces of falling wages and the aggressive advertising and marketing of products they would never be able to afford. There would only be two possible long-term outcomes: revolution, or the ruling classes would be forced to pay substantially higher wages to workers. To corporate elites, the latter choice would be too unpalatable to countenance.
The typical American family cannot live within its means because it cannot earn enough to sustain its lifestyle. Were it to downgrade its living standards to a level it could afford, there wouldn’t be enough consumer spending to drive the economy. This would force further personal austerity. Eventually we’d all be living outside.
You know what’s funny? Unlike the American family, the U.S. government can spend less than it earns. It can increase revenues by raising taxes. Unlike families, it spends trillions of dollars on stuff—wars—that it doesn’t need and actually makes things worse.
It could even use its power to force employers to pay workers what they deserve. If the government did that, families might not need credit.
They could (finally) live within their means.
(Ted Rall is the author of “The Anti-American Manifesto.” His website is tedrall.com.)
COPYRIGHT 2011 TED RALL