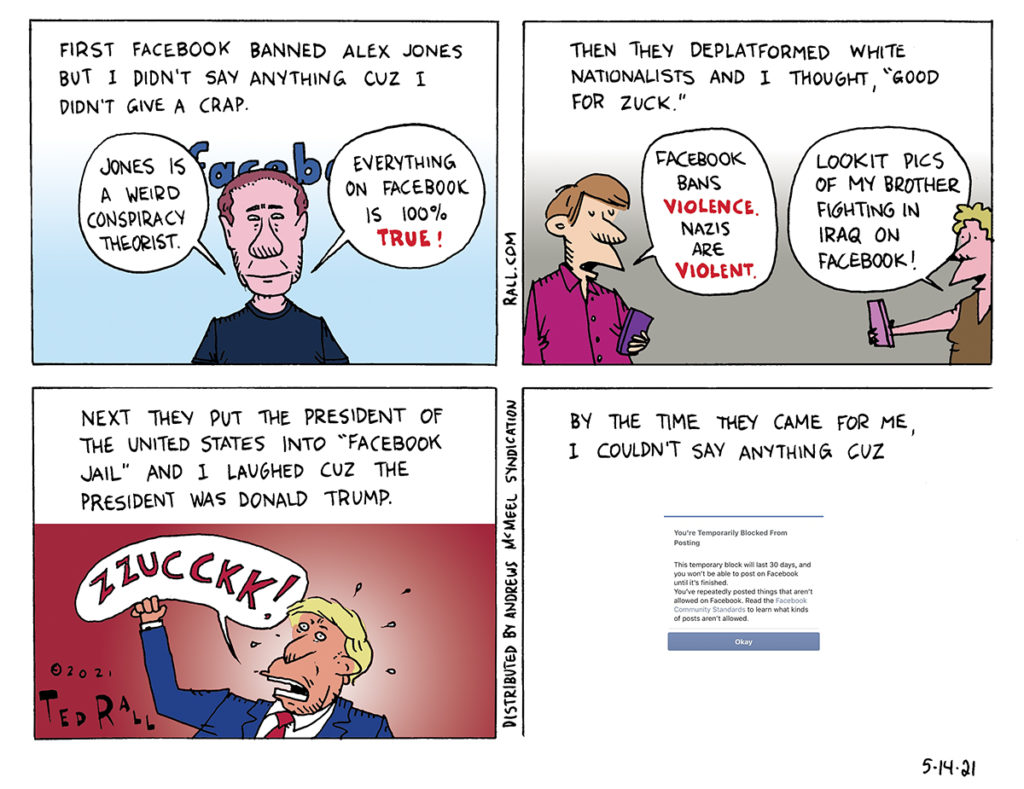
Liberals celebrated a decision by the Facebook review board to confirm the social media company’s decision to ban former president Donald Trump following the January 6 Capitol Hill insurrection. But if they can do it to the President of the United States, they can definitely do it to you too.
I Am a Victim of Republican Cancel Culture

The debate over “cancel culture” centers around how Democratic Party, “woke” activists and politically-correct “social justice warriors” expel people from social acceptability or force them into joblessness because something they said or did provoked an online mob.
But Republicans have been canceling people for much longer.
I am living proof.
My career grew to national prominence during the 1990s. By the time Bill Clinton left office, my cartoons and columns regularly appeared in well over 100 American newspapers and such magazines as Time, Fortune and Bloomberg. My editor at the New York Times added up the paychecks and calculated that his newspaper had published more cartoons by yours truly than by any other artist throughout the decade. I had a talk show on KFI radio, a 50,000-watt megastation in Los Angeles. I won major journalism awards, including two RFKs and a Pulitzer finalistship.
Because my cartoons and columns criticized Bill Clinton and the Democrats, the right-wing censorship squads let me be. They didn’t notice that I attacked Democrats from the left. My editor at the Pittsburgh Tribune-Review, a notorious right-wing rag owned by conservative billionaire Richard Mellon Scaife, loved my stuff even though I raged against NAFTA. “You sure know how to stick it to Bill and Hillary!” he beamed. Mm-hm.
I didn’t change my politics or my style after Bush became president. After 9/11, however, I went after Republicans because they were in power. So right-wing cancel culture goons targeted me for elimination.
My website contained a list of newspapers that ran my cartoons. GOP chatrooms and so-called “warbloggers” reproduced my client list, urging Republicans from around the country to pose as angry local subscribers. Fake subscribers demanded that my work be canceled via cut-and-paste complaint email forms the bloggers and their bots helpfully provided. I took my client list offline after my cartoon syndicate figured out their scheme. But many naïve editors kowtowed to the fake readers and canceled me.
Corporate cancel culture was relatively cold, ruthless and willing to overlook the profit motive in order to promote right-wing propaganda. Radio insiders said that high ratings guaranteed your freedom of expression. Despite my strong ratings, however, I was fired after KFI got acquired by Clear Channel Communications, the right-wing home of Rush Limbaugh. “They don’t want lefties on the air,” my program manager explained. “They’re willing to lose money. Anything to censor liberals.” My replacement was unpopular; they didn’t mind.
Even liberal media outlets yielded to cancellation campaigns orchestrated by the extreme Right. Yielding to a chorus of outrage ginned up by Fox News’ Bill O’Reilly and Sean Hannity over a cartoon in which I lampooned the marketing of the war on terror, The New York Times canceled me in 2002. “We thought the subject matter was inappropriate, and do regret that it did run,” a sniveling spokesperson told the Rupert Murdoch-owned New York Post.
The Times’ regular subscribers hadn’t made a peep for a week before Hannity’s army of fools drowned the Grey Lady in cut-and-paste postcards mailed in from flyover country. But Times editors didn’t notice. Nor did they take responsibility for choosing to publish my work. I was memory-holed. The editor who approved my work remained.
In 2004 it was the Washington Post’s turn to throw me to the braying Republican hounds.
Throughout the Bush years my income shrank. No radio station would have me. I was no longer shortlisted for journalism prizes. It became increasingly difficult to get published. I received fewer invitations to speak in public.
You can easily check it out yourself, or you can take my word for it: it’s not like my work got worse. I write better now, I draw better, I speak better than I used to. What changed was that gatekeepers at American media outlets became gun-shy. They would rather publish bland material that doesn’t elicit a response than a strong opinion that generates controversy. Who can blame them? Right-wing cancel warriors, no longer content to get leftie content banned, harass and threaten editors who run it.
No account of a cartoonist’s shrinking client list over the past 20 years would be complete without noting the financial meltdown of print media in general, brutal budget cuts and a widespread practice of laying off the cartoonist first. That goes double for left-leaning commentators who have found themselves out in the cold as the 50-yard line of American politics steadily moved to the right under Republican and Democratic administrations alike.
The same thing happened on TV. ABC canceled Bill Maher; MSNBC fired Phil Donahue, Keith Olbermann and Ed Schultz, all for being too liberal.
Everyone in the media has suffered. But right-wing cancel culture accelerated both of those trends.
I have adjusted to the new media landscape. It’s tough going, but I still have a viable career.
But don’t let anyone think Republican cancel culture isn’t a thing. It is.
And it has won.
Even though there are more socialist voters than either Democrats or Republicans, the Left is out in the cold. 39% of American voters prefer socialism to capitalism. Bernie Sanders’ approval rating is 49%, which is ten points higher than Joe Biden or Kamala Harris. Yet no newspaper in the United States employs a columnist or a cartoonist who endorsed Sanders or admits to being a socialist. Nor does any cable news network employ such a host or frequent contributor. This is not normal or OK. A nation with a vibrant and free news media represents a diversity of opinion. In this respect American news outlets are more rigidly censored than those of authoritarian regimes with state-controlled media.
I oppose left-wing cancel culture. I spoke out against liberal boycotts of companies that advertised on Rush Limbaugh and Dr. Laura Schlesinger. Censorship is toxic whether it comes from the left or the right.
Mostly, though, it comes from the right, and liberals go along with it.
(Ted Rall (Twitter: @tedrall), the political cartoonist, columnist and graphic novelist, is the author of the upcoming graphic novel about a journalist gone bad, “The Stringer.” Now available for pre-order. You can support Ted’s hard-hitting political cartoons and columns and see his work first by sponsoring his work on Patreon.)
The New York Times Called a Famous Cartoonist an Anti-Semite. Repeatedly. They Didn’t Ask Him for Comment.

Earlier this year the Portuguese cartoonist António Moreira Antunes drew one of the most controversial political cartoons in history. His cartoon about U.S.-Israeli relations sparked so much controversy that The New York Times, whose international edition published it in April, decided to fire its two staff cartoonists, neither of whom had anything to do with it. Then the Times permanently banned all editorial cartooning.
Antunes took the most flak from the Times itself, as it furiously backpedaled from its own editorial decision to publish his cartoon. In five news stories and editorials, the Newspaper of Record unreservedly described Antunes’ cartoon as anti-Semitic. American media outlets followed the Times’ lead.
“I’m not anti-Semitic, I’m anti-Zionist,” Antunes told me. “In the Israeli-Palestinian conflict I am in favor of two countries and I am against all annexations made by Israel.” The Times censored Antunes’ side of the story from its readers.
Was Antunes’ cartoon, a metaphorical illustration depicting Israeli prime minister Benjamin Netanyahu as a dog leading a blind President Trump, anti-Semitic? That question is both inherently subjective and eminently debatable. “The cartoon is not anti-Semitic, but many political and religious sectors classify any criticism of Israeli policies as anti-Semitic,” Antunes said in an interview.
Pro-Israel groups disagreed. On the other hand, many cartoonists thought there was nothing wrong with it.
But that’s not how the Times covered it. In article after article, Antunes’ cartoon was described as anti-Semitic. It was an objective truth. No one could doubt the cartoon’s anti-Semitism more than the fact that Washington is the capital of the United States.
“Times Apologizes for Publishing Anti-Semitic Cartoon,” read the headline on April 28th.
Not “allegedly anti-Semitic.”
Not “cartoon criticized as anti-Semitic.”
In an April 30th editorial, the paper called Antunes’ work “an appalling political cartoon” and “an obviously bigoted cartoon.” It explained: “The cartoon was chosen from a syndication service by a production editor who did not recognize its anti-Semitism.” Not “its possible anti-Semitism.”
Two more articles on the subject appeared on May 1st: “Times Disciplines Editor and Cancels Cartoon Contract Over Anti-Semitic Drawing” (we don’t know what that discipline entailed, but unlike the cartoonist, the editor wasn’t fired) and “After the Publication of an Anti-Semitic Cartoon, Our Publisher Says We’re Committed to Making Changes.” The text of both pieces described the cartoon as self-evidently anti-Semitic.
On June 10th a Times article announced the end of political cartooning in the Gray Lady. Antunes’ cartoon, the Times stated flatly, contained “anti-Semitic imagery.”
Accusing a political cartoonist of anti-Semitism is as serious as it gets. So something jumped out at me as I read the Times’ repeated characterizations of Antunes’ cartoon as anti-Semitic, so devoid of mitigating language: where was his response?
“The New York Times never contacted me at any time,” Antunes now says.
I reached out to the Times about this; I asked why they didn’t talk to him and how the paper made the determination that Antunes’ cartoon was anti-Semitic. James Bennet, the editorial page editor who banned cartoons and presumably wrote the editorials, did not reply to my repeated queries. (I gave him nearly a week to do so.) Neither did two reporters who authored pieces about Antunes.
I did hear back from Stacy Cowley, who wrote the April 28th piece. “I dug around online and was unable to find any contact information for Mr. Antunes,” Cowley explained. “He has no publicly posted contact information that I could find, and as of the date I wrote my article, he had not publicly commented to any other news outlets about his cartoon. (Had he done so, I would have linked to and quoted his comments.)” Cowley said she tried to reach the editors of Antunes’ home paper in Portugal. She noted that she was working on a tight deadline.
I reached Antunes via Facebook; he replied via email.
Contacting the subject of a news story for comment is Journalism 101, a basic ethos taught to students at high school newspapers. That goes double when the article is critical.
“Few writers need to be reminded that we seek and publish a response from anyone criticized in our pages,” the Times says in its Guidelines on Integrity. “But when the criticism is serious, we have a special obligation to describe the scope of the accusation and let the subject respond in detail. No subject should be taken by surprise when the paper appears, or feel that there was no chance to respond.” Given the gravity of the criticism leveled against Antunes, the Times appears to have fallen woefully short of its own standards.
OK, Cowley was on deadline. What about the other articles? They appeared days later. One ran six weeks later. Antunes isn’t a recluse—he’s one of the most prominent cartoonists in Europe. I found him. So did other newspapers.
The Times could have contacted the New York-based syndicate from which it bought Antunes’ cartoon; the syndicate has his contact information, as they do of all their contributors.
Though scarred by his experience, Antunes says that he has not lost business. “The U.S. media” he says, “are prisoners of political correctness, right-wing turning [sic] and social media.” Europe, he says, is more tolerant.
What’s clear is that the Times threw its cartoonist under the bus in a shockingly cavalier fashion—a practice that has become so common that it’s contributing to the imminent extinction of political cartooning.
The Times owes Antunes an apology. They owe the two fired cartoonists their jobs back, along with back pay. Political cartoons should resume their rightful place in the paper.
Finally, the Times owes its readers an assurance that they will never again succumb to the siren call of “fake news” as part of an ethically-challenged witch hunt.
(Ted Rall (Twitter: @tedrall), the political cartoonist, columnist and graphic novelist, is the author of “Francis: The People’s Pope.” You can support Ted’s hard-hitting political cartoons and columns and see his work first by sponsoring his work on Patreon.)
Freedom of the Press? Not in the U.S.
![]()
The United States ranks 48th among nations for press freedom, according to Reporters Without Borders. Since few other countries have the equivalent of our First Amendment, learning that we rank below Botswana and Slovenia may come as a surprise.
Mostly the organization pins this dismal state of affairs on Trump’s attacks on the news media. They reference the White House’s revocation of CNN reporter Jim Acosta’s press card, the president’s “fake news” and “enemy of the people” jibes and his tacit approval of the grisly murder of Washington Post columnist Jamal Khashoggi by the government of Saudi Arabia. “At least one White House correspondent has hired private security for fear of their life after receiving death threats, and newsrooms throughout the country have been plagued by bomb threats and were the recipients of other potentially dangerous packages, prompting journalism organizations to reconsider the security of their staffs in a uniquely hostile environment,” reports RWB. (Cry me a river! I’ve received hundreds of death threats.)
Like most other mainstream analyses of the state of press, RWB focuses on how easy it is for large, corporate-owned media conglomerates with establishmentarian political orientations to do their jobs.
Independent journalists, especially those whose politics are left of the Democrats or right of the Republicans, have much bigger problems than deep-pocketed mega-conglomerates like CNN.
No consideration of freedom of the press in the U.S. is complete without a hard look at the case of Julian Assange. The founder and publisher of WikiLeaks is rotting in an English prison, awaiting extradition to the United States for possession and dissemination of classified information—exactly what The New York Times did when it published the Pentagon Papers and the Edward Snowden revelations. He is being “treated worse than a murderer, he is isolated, medicated,” says journalist John Pilger, who recently visited him. Incredibly, corporate media is siding with the Trump Administration, not merely ignoring Assange but mocking him and accusing him of treason (which is impossible, since he’s not American).
Censorship is insidious; readers and viewers can’t know what they’re not told. Almost as sinister as the persecution of Assange is the wholesale erasure of left-wing politics from U.S. news media. 43% of Americans tell pollsters they want the U.S. to become a socialist country. 36% of registered Democrats currently support self-described “democratic socialist” Bernie Sanders or Elizabeth Warren, whose campaign promises closely align to Sanders’.
The nation’s 1,000-plus newspapers employ countless Democrats and Republicans. But there isn’t a single staff columnist or editorial cartoonist who agrees with that 43% of the public that socialism would be better than capitalism. There isn’t a single one who says he or she supports Sanders or Warren.
Watch CNN, MSNBC, FoxNews and the other cable news outlets. Once in a very long while you might catch a token leftist joining a yakfest. You’ll never see socialist get a gig as a regular contributor, much less be asked to host a show. If you don’t think it’s weird that 43% of the country’s population is being censored, I don’t know what to tell you.
Pervasive among both corporate and independent journalists is self-censorship. Apologists say that freedom of the press doesn’t include the right to be published, and that’s true. Because journalists are like everyone else and can’t survive without earning money, however, the real-world practical effect of having to earn a living is that reporters and pundits have to watch what they say lest they become unemployable pariahs like I was after 9/11. “Sorry, man,” an editor I considered a friend told me after I asked him for work at his business magazine, “you’re radioactive.”
The Washington Post and other corporate news companies ridiculed Bernie Sanders’ recent assertion that Amazon CEO Jeff Bezos’ ownership of the Post influences its coverage. As Sanders noted, it’s not like Bezos calls Post editors to tell them what to print and what to censor.
Self-censorship is subtle. Post executive editor Marty Baron is technically correct when he retorts that “Jeff Bezos allows our newsroom to operate with full independence.” But he’s dodging the meat of the matter. Baron and other Post editors know who their bosses are: Bezos and, more generally, his allies in the corporate ruling class. No matter how much they protest that they can follow any lead and print anything they want, that knowledge of who butters their bread informs every move they make. It’s why, when the editorial page editor sorts through the day’s nationally syndicated political cartoons, he never ever publishes one from a left-wing political orientation, no matter how well-written or well-drawn it is. It’s why, when they’re hiring new staffers, they never hire a leftie. They’re smart enough not to bite the hand that feeds them. It’s also why the person making that hiring decision is not himself or herself one of the 43%.
I’m more audacious. Yet I too know not to go too far.
I’ve learned that I can draw a cartoon or write a column criticizing “free trade” agreements without fear of getting fired or assassinated. There is also no fear that it will be published by a corporate newspaper—so why bother? Over the long run, I have to give editors material they want to publish; if I send out too much stuff about a verboten topic like free trade I’ll lose clients.
Most people who hear about my defamation lawsuit against the Los AngelesTimes support me. But most people don’t hear about it for a simple reason: when one member of the press is besieged—especially when it’s justified—the others circle the wagons. Reporters for The Washington Post, The New York Times and fake-left outfits like The Intercept contacted me eager to write about how the LAPD pension fund bought the Los Angeles Times in 2014 and then ordered the paper to fire me because I criticized the police in my cartoons. (It’s still legal for the the cops to buy a newspaper.) Invariably they went silent after talking to their editors.
Corporate gangsters stick together.
As I said, I’m not that brave. My editor didn’t tell me about the LAPD deal with the Times. I assume she didn’t know. If she had called and said “hey, lay off the police, they own us now, draw about something else,” I would have. I have to make a living.
48th? When it comes to press freedom, the U.S. is benefiting from grade inflation.
(Ted Rall (Twitter: @tedrall), the political cartoonist, columnist and graphic novelist, is the author of “Francis: The People’s Pope.” You can support Ted’s hard-hitting political cartoons and columns and see his work first by sponsoring his work on Patreon.)
Media Censors the Opinions of 37% of Americans. And Now They’re Gloating About It.
Thirty-seven percent of American citizens are socialist or communist. That’s far more people than voted for either Hillary Clinton (28% of eligible voters) or Donald Trump (27%) in 2016.
The majority is voiceless. A privileged minority rules. The United States is a political apartheid state.
If the Left were allowed on the ballot in this fake democracy, given space in newspapers and on television, invited to join political debates, and if it wasn’t brutally suppressed by the police and FBI, the Left wouldn’t need to wage a revolution in order to take over the country. Leftists could easily win at the ballot box if America were a real democracy.
Media censorship plays a major part in the conspiracy to deny the majority Left its rightful role as the nation’s rulers. Socialist and communist Americans read newspaper editorial pages and draw the false conclusion that they’re members of a lunatic fringe. More than 1,000 papers—yet not one single leftist opinion columnist or editorial cartoonist on staff?!?
Leftist Americans exist by the millions but many are isolated from one another. They watch CNN, MSNBC and FoxNews and figure they’re all alone. None of the three major cable news networks employs a single left-wing commentator. They go to the polls but there’s no left party on the ballot. Or if there is, they’ve never heard of it and don’t want to waste their votes.
To be a Leftist in America today is analogous to how black people felt until recently while watching TV: you don’t see anyone like you. The powers that be want you to feel like the Invisible Man, as though you didn’t exist. You know you exist. But you can’t miss the system’s message that you don’t matter.
American politics is a party to which you have not been invited.
This has been the state of affairs for as long as I can remember. Even as more Americans become disgusted by runaway capitalism, censorship of the Left has become increasingly thorough and ferocious.
There used to be a little space. In the 1990s lefties like me were granted occasional mentions in The New York Times, Washington Post, CNN and NPR. Even FoxNews had us on to serve as punching bags. Shortly after 9/11 we disappeared along with the Twin Towers, relegated to a few blogs and alternative weeklies. Now newspapers and cable TV news and corporate news websites never give space or air to representatives of the Left. (Don’t email me about AOC. She’s a Democrat, not a leftist.)
Censorship of the really-existing Left is impressively thorough. You’ll find exactly as much opposition to the government on the media here in the U.S. as you’ll find in North Korea.
Ashamed and afraid, the gatekeepers used to have the decency to keep secret their suppression of people whose political sin is that they really, truly believe that all humans are equal. They didn’t even think they were biased. They thought they were reasonable. Moderate. Middle of the road.
Censorship with a smile is no longer enough for America’s corrupt news media. Now they’re brazenly contemptuous. The bastards even seek to elevate censorship of the Left to a proud American value!
On May 12th the Times ran another in a string of hit pieces on RT America, a television network it described as “the cat’s paw of Russia’s president, Vladimir Putin.” RT, the Times complained, “amplifies voices of dissent, to sow discord and widen social divides. It gives the marginal a megaphone and traffics in false equivalence.” Imagine that: giving airtime to people we’ve always censored! “Voices of dissent” must never be “amplified.” They must be silenced.
This has become a standard talking point.
“RT America has a modest audience, exploring stories of dissent, injustice and poverty within the U.S. that it says American news outlets ignore,” NPR sneered in 2016, as if dissent, injustice and poverty were standard fare on corporate media outlets. Anyway, if RT’s audience is so small, why is the political establishment so worried about them?
The formerly-liberal Guardian has gotten into the act: “Fringe opinion takes centre stage [on RT],” it wrote in 2017. “Reporting is routinely bolstered by testimony from experts you have never heard of, representing institutions you have never heard of.” It is true that RT rarely interviews “experts” like John Bolton and William Kristol, neocon architects of the Iraq War who despite their evil idiocy pop up everywhere from CNN to the Bill Maher show. Far more often, they interview people who have been right year after year about issue after issue—people like me.
I get interviewed by RT often. (Disclosure: I am a frequent guest on RT’s sister radio network Sputnik News and draw cartoons for them too.) Never once have they told me what to say or not say. I wish I could say the same about many “mainstream” U.S. media outlets.
Many attacks against RT originate with the U.S. government’s national security apparatus. The Times piece blithely cites the RAND Corporation, Molly McKew, a right-wing lobbyist for the anti-Russian government of Georgia, and the Director of National Intelligence to support its allegations. A 2017 report issued by the DNI groused: “RT’s reports often characterize the United States as a ‘surveillance state’ and allege widespread infringements of civil liberties, police brutality, and drone use. RT has also focused on criticism of the U.S. economic system, U.S. currency policy, alleged Wall Street greed, and the U.S. national debt.”
Notably, the report did not question the accuracy of those assertions.
It certainly didn’t suggest that the U.S. stop doing all those things that make it look so awful.
To U.S. corporate propagandists the solution is clear: censor more and censor better.
Make censorship good.
(Ted Rall (Twitter: @tedrall), the political cartoonist, columnist and graphic novelist, is the author of “Francis: The People’s Pope.” You can support Ted’s hard-hitting political cartoons and columns and see his work first by sponsoring his work on Patreon.)
Journalists Had Better Hope I Win My Case Against the Billionaire-Owned L.A. Times

I have written extensively about my lawsuit against the LA Times. As I prepare for the next, do-or-die, stage of my case, it’s time to explain why Rall v. Los Angeles Times et al. has broad implications beyond me personally.
Freedom of the press is at stake.
The subtle yet fundamental question here is: who needs freedom of the press? The obvious answer is journalists: reporters and pundits. But journalists’ freedom to report and editorialize is in grave danger from a surprising enemy: their employers.
Once was, reporters like Woodward and Bernstein were on the same side as their employers. In this age of corporate aggregation of newspapers and other media outlets by publicly-traded media corporations and individual billionaires, however, newspapers and other media outlets are often compromised by their quest for profits, as the LA Times’ parent company was when it allowed its stock to be sold to the LAPD pension fund. In this struggle the media companies have framed themselves as guardians of press freedom at the expense of journalists, ironically securing the power to screw journalists in the guise of First Amendment protections.
If the California Supreme Court refuses to hear my case — which is probably what will happen — or hears it and rules for the Times’ anti-SLAPP motion against me, the court will send a chilling message to journalists and pundits across the country. Most Americans, and most reporters, live in states with anti-SLAPP statutes modeled on California’s.
The threat to journalists is unmistakable: rock the boat and you risk being destroyed.
Write an article critical of a powerful institution like the LAPD, the nation’s highly militarized, largest and most brutal police forces, controlling a $16 billion pension fund, and they can pull strings to get you fired. It can also happen in a tiny town like Baker City, Oregon.
Even worse, you can’t find another job because they use falsified “evidence” to smear your reputation for honesty. Even if you can prove that it’s BS — as I did — media companies use their editorial endorsements of jurists and politicians to rig the courts with their allies so you, the victim, get dunned hundreds of thousands of dollars for the villainous media company’s legal fees!
I have advice for journalists thinking about covering police abuse: don’t. The price for doing your job — termination, defamation and bankruptcy — isn’t worth it.
If I could go back to 2015 when the LAPD-owned LA Times trashed my reputation in service to a thin-skinned police chief, I would not draw or write anything about the cops. It’s too dangerous.
I have learned how big media companies have stacked the bench with sympathetic judges, lobbied for laws that protect them from accountability for breaking the law and used their influence to crush individual journalists for such crimes as reporting the news or having worked long enough to earn a high salary. The system doesn’t even pretend to be fair. Many judges are former prosecutors; how can they justify not recusing themselves from cases involving the cops?
Now there is a $330,000 judgment against me for having the gall to defend my reputation in court. Unless the California Supreme Court overrules it, that judgment will be final and will grow bigger. Journalists and pundits aren’t covering my case — they’re afraid, as they ought to be — but they are watching. If the judgment stands, who will be stupid enough to take on the LAPD or similar institution?
As if the chilling effect on journalists wasn’t enough reason to watch my case, the Times is arguing (so far, successfully) that media companies should no longer extend protections against discrimination by gender, age and sexual orientation to their workers. Unless the court overturns the lower court rulings against me, the door will be pushed open for the Times and other California media corporations to fire, say, its African-American or transgender employees without redress in the courts.
Then there’s the damage to defamation law. For hundreds of years it has been possible for a person wrongfully slimed by a news publication to go to court to try to clear their name. Abusive anti-SLAPP motions have made a mockery of libel law to the point that the National Enquirer, represented by the same lawyer as the Times, falsely claimed Richard Simmons had become a transsexual woman and Simmons was ordered to pay $130,000 to the Enquirer!
It should be challenging to sue for libel, not impossible.
“The quote/unquote truth doesn’t matter,” Los Angeles Times/National Enquirer lawyer Kelli Sager said in court. So far, she’s been right. Judges have bent over backwards to believe the Times’ many lies and ignore the plain truth right in front of them. Hopefully a court outside LA will let me get my day in court.
(Ted Rall, the cartoonist, columnist and graphic novelist, is the author of “Francis: The People’s Pope.” You can support Ted’s hard-hitting political cartoons and columns and see his work first by sponsoring his work on Patreon.)
SYNDICATED COLUMN: Don’t Fall for the First Amendment = Free Speech Trick

Like climate change, this is one of those problems I keep expecting people to wise up about but — because they never do — it keeps getting worse.
Thus this tutorial.
The problem is that too many Americans conflate the First Amendment with free speech.
You see it when people discuss the current social-media crackdown against controversial right-wing radio talk show host Alex Jones and his website InfoWars. Jones was banned by Facebook, YouTube (which is owned by Google), Apple and Spotify, and more recently suspended by Twitter for one week. Writing in The New Yorker Steve Coll mocked Jones for calling himself the victim of “a war on free speech.”
“Such censorship is not unconstitutional,” Coll reminds readers. “The First Amendment protects us against governmental intrusions; it does not (yet) protect speech on privately owned platforms.”
The U.S. government is rarely in a position to censor Americans’ freedom of expression. Because the vast majority of censorship is carried about by non-government entities (like the social media companies blocking Jones) the First Amendment only bans a tiny portion of censorship.
Some government agencies do censor the press. A federal judge ordered The New York Times to halt publication of the Pentagon Papers in 1971. The LAPD, whose pension fund owned part of the parent company of The Los Angeles Times and was angry about my work criticizing its brutality and incompetence, ordered the Times to fire me as its cartoonist. They complied. Annoyed by an editorial in the local paper criticizing them for conducting random searches of high school students at basketball games using dogs, the police in Baker City, Oregon created a fake dossier of crimes committed by the editorial writer, which they used to get him fired from his job.
These cases are covered by the First Amendment. But they are outliers.
We can’t protect existing rights if we don’t understand the current parameters of the law. New rights arise from unfulfilled political needs and desires; we can’t fight for expanded protections without defining what is lacking yet desired. Schoolchildren and student journalists, both public and private, are constantly running up against censorship by teachers and administrators. Employers constrain political speech, obscenity and other forms of expression on the job. These are free speech but not First Amendment issues.
In recent decades opponents of free speech, mostly but not exclusively on the right, have relentlessly conflated First Amendment debates with those over free speech. The effect has been to reduce society’s expectations of how much freedom we ought to have to express ourselves.
Take the Jones case.
Writing for the website Polygon, Julia Alexander provides us with a boilerplate (liberal) response to Jones and his allies’ complaints that the big social media companies are suppressing his free speech. First she described some of the episodes that prompted banning Jones, such as pushing PizzaGate and Sandy Hook shooting denialism. Then she pounces: “It’s not a freedom of speech issue, nor one of censorship,” Alexander writes. “The First Amendment…gives American citizens the freedom of speech…The United States government isn’t bringing the hammer down on Jones. This isn’t a political issue, as badly as Jones might want to pretend otherwise.”
See what Alexander did? In just a few sentences she squeezes and smooshes the extremely broad practice of “censorship” into the relatively tiny box of “the U.S. government…bringing the hammer down.” I don’t mean to pick on her — I’ve seen this same exact ball of sophistry used over and over by countless other pundits.
Of course Twitter, Facebook et al. are censoring Jones. Of course the First Amendment doesn’t cover him here. Obviously it’s a freedom of speech issue. The question — the question pro-censorship folks like Alexander doesn’t want us to ask — is, is it right?
For what is right is not always what is legal (see: slavery). Alex Jones and his allies may or not be legit. Their political arguments often are not. But the question they’re asking here is legit and important: should companies like YouTube have the power to suppress speech — any kind of speech?
Alexander ends with a message you ought to find chilling: “Don’t publish vile content, and your video will probably be a-ok.”
“Probably”?
Who gets to define “vile”? Alexander? Mark Zuckerberg, apparently.
Obviously it is a political issue. But that’s not the main point here.
Free speech used to belong to the man with the means to buy ink by the barrel. Now you can buy a newspaper for pennies on the dollar, but who will read it? Much if not most of the political debate in our civic life takes place on platforms owned, controlled and censored by the companies blocking Jones’ content. They write and enforce their own rules. As private companies they are unaccountable to we, the people. We don’t know how they make censorship decisions or who makes them.
Perhaps this is a splendid state of affairs. Maybe Americans don’t mind surrendering control of political debate to faceless tech giants.
Whatever we decide, however, we deserve a transparent discussion. We ought not to let ourselves be fooled into falsely equating free speech to the First Amendment. Free speech means exactly that: everyone and anyone can say anything at all, anywhere they please, to anyone.
Every First Amendment case is a free speech issue. But only a tiny fraction of free speech issues is a First Amendment case.
(Ted Rall (Twitter: @tedrall), the political cartoonist, columnist and graphic novelist, is the author of “Francis: The People’s Pope.” You can support Ted’s hard-hitting political cartoons and columns and see his work first by sponsoring his work on Patreon.)
Distributed by Creators Syndicate
(C) 2018 Ted Rall, All Rights Reserved.
SYNDICATED COLUMN: No Way Would Today’s Newspapers Publish the Pentagon Papers

Steven Spielberg’s new movie “The Post” depicts a newspaper’s decision to defy the government, risk its financial health and imprisonment of its editors in order to report a hard truth and defend the press’ First Amendment rights by publishing the Pentagon Papers.
After the Washington Post’s decision to inform the American people that top government officials had known that the Vietnam War was unwinnable yet had repeatedly lied about it for years, editor Ben Bradlee (played by Tom Hanks) dumps a pile of out-of-town newspapers on a desk for publisher Katharine Graham (Meryl Streep) to see. We’ve started a “rebellion,” Bradlee informs Graham. We’re no longer alone speaking truth to power.
No way would that happen today.
I was pleased to see that “The Post” highlights the pressures and biases that weighed against publication: a publisher undermined by sexism and low expectations, a paper trying to raise capital under the eye of nervous bankers, the Nixon Administration’s take-no-prisoners prosecutorial abuse by a vicious attorney general, and — not least — the Post’s cozy establishmentarianism, centered around Graham’s famous hard-drinking salons where reporters hobnobbed with the officials they were supposed to cover objectively.
After a lot of wavering and gnashing of lawyerly teeth, Graham finally makes the call: go to press.
The key point of this story, which isn’t made in the movie and few younger moviegoers are likely to be aware, is that it was her decision to make. The Graham family held controlling interest in the Washington Post Company. Great newspaper families like the Grahams, the Chandlers and the Sulzbergers were quirky and often had bad politics. But they also had something today’s corporate, publicly-traded media outlets do not: editorial freedom.
They didn’t always do the right thing. But they could. So sometimes they did.
Sadly, those days are gone.
Amazon CEO Jeff Bezos, reportedly a right-leaning libertarian, bought the Post in late 2013. What reception would a Daniel Ellsberg (who leaked the Pentagon Papers) or an Edward Snowden get if they contacted a Post reporter today, under Bezos?
Snowden’s case is indicative. The Post and three other papers published Snowden’s NSA leaks in 2013, months before Bezos took over. In 2016, the Bezos-owned Post called upon President Obama to refuse Snowden’s pardon application. In so doing, wrote Glenn Greenwald, the Post “achieved an ignominious feat in U.S. media history: the first-ever paper to explicitly editorialize for the criminal prosecution of its own source — one on whose back the paper won and eagerly accepted a Pulitzer Prize for Public Service.” (The other three papers were pro-pardon.)
Even more obnoxiously, the Post’s Snowden editorial didn’t mention its major conflict of interest related to intelligence agencies like the NSA. Amazon — the Post’s sister company under Bezos — had the CIA (where Snowden also worked) as a $600 million client. That’s more than twice what Bezos paid for the Post.
Coincidence? Je pense que non.
The Los Angeles Times sells “Speaking Truth to Power” hoodies. But when the power is the LAPD — and the LAPD owns the paper — the Times publishes lies.
My regular readers are familiar with the sordid details of my 2015 firing by The Los Angeles Times as a favor to LAPD Chief Charlie Beck. You’re not much of a political cartoonist in L.A. if you don’t go after the militarized, racist, violent LAPD — and the Times published many of my anti-LAPD/anti-Beck toons over the years. So did the Pasadena Weekly, which drove the boys in blue so nuts that they asked its publisher to fire me. PW refused.
Then the Times’ corporate parent, the Chicago-based Tribune Publishing, hired an LAPD-connected billionaire and wannabe politician, Austin Beutner, as publisher for the Times. Beutner appears to have midwifed a deal in which the LAPD patrolmen’s $16.4 billion union retirement fund moved to a firm that invested eight figures into a fund containing Tribune stock. (Given that newspaper stocks in general and Tribune specifically had been losing value, it’s a fair assumption that the buy was more about influence than taking care of retired LAPD officers.) Within weeks — and explicitly against Times rules — the same union issued an award to Beutner for his “support [of] the LAPD in all that they do.”
Beck asked his friend Beutner to use ginned-up “evidence” to fire and smear me; Beutner, the cop-award winner, complied, and even stayed the course after the truth came out and I was vindicated. My defamation case against Beutner and the Times is in court.
The Times never disclosed to its readers about Tribune’s business relationship with the LAPD union.
It’s a level of corruption that would make Al Capone blush. Yet it’s perfectly legal in the United States for a police union to buy a newspaper. Indeed, the same union bought part of the San Diego Union-Tribune in 2009 — and leveraged its ownership to ask that the U-T fire critics of the police.
Come to think of it, isn’t it weird that a company with more than half a billion dollars in business with the CIA is allowed to own a major news organization like the Post?
Given the Trump Administration’s attacks against “fake news” and the news media, it may seem paradoxical to suggest government action as a solution to the corruption of the news media as we’re seeing at outlets like the Washington Post and Los Angeles Times. But the evidence is clear. Outrageous deals such as those between the Post’s owner and the CIA and between the Times’ owner and the LAPD amount to government censorship of the news media — a violation of the First Amendment’s fundamental principle.
Congress should prohibit such arrangements.
(Ted Rall’s (Twitter: @tedrall) brand-new book is “Meet the Deplorables: Infiltrating Trump America,” co-written with Harmon Leon. His next book will be “Francis: The People’s Pope,” the latest in his series of graphic novel-format biographies. Publication date is March 13, 2018. You can support Ted’s hard-hitting political cartoons and columns and see his work first by sponsoring his work on Patreon.)
SYNDICATED COLUMN: The Pledge of Allegiance is anti-American

Right-wingers conflate nationalism with patriotism. But they’re not the same thing. Patriots love their country because it does good things; for nationalists it’s our country right or wrong. A lot of stuff nationalists call patriotic couldn’t possibly be more un-American.
The singing of the national anthem before sporting events, and the reciting of the Pledge of Allegiance, are prime examples.
The latest nationalism vs. patriotism controversy arrives courtesy of Colin Kaepernick, the African-American pro football player blackballed by the NFL for kneeling in silent protest over police shootings of blacks rather than stand for the signing of the national anthem alongside his teammates and fans before games. The “take a knee” movement has spread throughout the league, largely in response to President Trump’s crude remark that those who refuse to stand during “The Star Spangled Banner” are “sons of bitches.”
At football games and similar events where the anthem is sung, standers far outnumber kneelers — and that’s weird. Because if one person is kneeling against police brutality, then it stands to reason that standing up means you support cops gunning down unarmed black people. Are there really that many racists?
That, and when you stop to think about it, the whole idea of rote rituals to prove our loyalty run completely counter to what most Americans, liberal or conservative, think their country is about.
As I have written before, lefties and righties don’t have the same ambitions for the U.S. Following the tradition of the French Revolution and the Declaration of the Rights of Man, the Left idealizes individual rights. They dream of a country where everyone is not only created equal, but treated accordingly. The Right values empire. Rightists’ ideal America is a global military and economic superpower.
Still, the two sides have something in common. They want to be left alone, to live their lives as free of government interference as possible. Progressives want the government out of their bedrooms. Traditionalists want it out of their incomes. Totalitarianism — a form of government whose control over citizens’ daily lives leads to the requirement that everyone attend one meeting after another and report dissent to the authorities — could no more catch on here than North Korean-style displays of signs flipped by synchronized flags or parades of military hardware (though Trump wants to start those).
Like the singing of the anthem at games, the Pledge of Allegiance reflects a totalitarian impulse you find in fascist and authoritarian regimes, not democracies. The U.S. and Canada are the only countries on earth where national anthems are played at the start of sporting events. Even in many authoritarian states, the requirement that children (and athletes) swear fealty to the nation (or, as here, its flag) would be considered too creepy to contemplate.
When your country is crazier than Zimbabwe, it’s time to take stock — even if you’re a Republican.
Other nations require oaths of allegiance from those taking public office, like members of parliament. Some ask the same of foreigners seeking to become naturalized citizens. But the U.S. may be the only nation on earth to have a widely-used pledge of allegiance.
Children who refuse to recite the Pledge of Allegiance are routinely punished, criticized and ostracized, even in public schools. I know — it happened to me in elementary school. Kaepernick, a top-tier athlete, has been denied employment. These are obvious violations of the all-American value of free speech and expression guaranteed by the First Amendment.
The addition of “under God” in 1954, at the height of the McCarthy era and its rancid loyalty oaths, further violates another core principle of Americanism, the freedom to worship as you please or not at all as protected under the Establishment Clause of the US. Constitution.
In one respect, however, the Pledge of Allegiance owes its origins to something that couldn’t be more American: a huckster out to make a few extra bucks.
Why do Americans pledge allegiance to the “flag,” as opposed to the nation or its government? It boils down to capitalist greed. The origins of the Pledge date to 1892, when James B. Upham, the marketing executive of the popular children’s magazine The Youth’s Companion used the 400th anniversary of Columbus’ arrival in the Americas to promote a conference in honor of the American flag. He pushed the Pledge in his magazine as a way to promote nationalism and sell flags to public schools. Schoolhouses purchased 26,000 flags the first year alone.
Kids reciting the pledge were supposed to raise their arms at the same time — yep, the Hitler “sieg heil” salute before Hitler. World War II put an end to that in American schools.
Having traveled extensively, I have observed that the countries whose governments insist upon the most extravagant displays of nationalism line up neatly with those with the least personal freedom. In authoritarian China and the police state of Turkmenistan, national flags and banners extolling slogans and quotes of the ruling party festoon every government office and pedestrian overpass. As Turkey moves away from democracy and closer to autocracy, Turkish flag stickers multiply on automobiles.
It is the opposite in the European democracies. A Frenchman who hung a French flag from his front porch would be ridiculed by his neighbors, socialist and Le Pen supporter alike. It is not that the French and the Dutch and the Spanish and other Europeans do not love their countries as much as Americans do; if anything, most Europeans are grateful that their countries are not like ours. They are patriots. And they remember World War II, when those who liked to wave flags and insisted on loyalty oaths to the state turned out to be dangerous.
Everyone should sit out the singing of the national anthem. It’s archaic and uncomfortably reminiscent of fascism.
It is time to leave the Pledge of Allegiance where it belongs, on the dungheap of history, remembered as a clever way to move piles of colored cloth.
(Ted Rall (Twitter: @tedrall) is author of “Trump: A Graphic Biography,” an examination of the life of the Republican presidential nominee in comics form. You can support Ted’s hard-hitting political cartoons and columns and see his work first by sponsoring his work on Patreon.)