One of the most persistent challenges faced by Kamala Harris’ abbreviated presidential campaign is a vexingly wide gender gap. Men just aren’t that into her.
Democrats have deployed several approaches to convince male voters to feel the joy.
Divide and conquer: Harris’ policies divvy up guys by race. Her “opportunity agenda for Black men” would offer special loans and internships to Black entrepreneurs (no word on whether that’s been lawyered for constitutionality), fund federal studies on sickle-cell anemia and other diseases that disproportionately affect Black men and give them priority to profit from the emerging legal marijuana business (note to Democrats: cannabis equity failed in New York). Harris’ “opportunity agenda for Latino men” (see a trend?) would offer Latino guys more small business loans. A Google search for “opportunity agenda for white men” comes up empty but hey, there are still a couple hours left in the race.
Kamala is also playing the class card. A spot for the Pittsburgh TV market features a Steelers fan and maintenance worker who calls himself a “yinzer” (Pittsburgh native). “Donald Trump does not care about the working man whatsoever,” he says. “He’s a little rich kid too; he ain’t me. Little silver spoon boy Donald Trump. How is he relatable to me whatsoever? The guy literally lives in a country club. Do I look like a country club kind of guy?” Don’t tell the yinzers that Harris, worth $8 million and a member of an exclusive country club with a $300,000 initiation fee, is more at home with the Trumps than with them.
Humor: A Harris super PAC made news with “Man Enough,” an ad that showcases six hypermacho dudes—evoking more than a smidge of homoeroticism (“my full-throated endorsement”)—who say they’re so butch that they eat “carburetors for breakfast” and aren’t “afraid of bears,” but also like chicks and plan to vote for Harris and support abortion rights. An official Harris ad depicts a burly Black finance bro who ditches his plan to refrain from voting after confronted by a passel of disapproving ladies. Ladies are doters for early voters!
Shame and guilt: Former president Barack Obama called out sexist men whom, he finger-wagged, “just aren’t feeling the idea of having a woman as president.” His wife Michelle helpfully reminded the XY set that “your wife and mother could be the ones at higher risk of dying from undiagnosed cervical cancer because they have no access to regular gynecological care.” As if men didn’t care about their wives, sisters, mothers and female friends.
This is a portrait of a campaign that wants men’s votes enough to embarrass itself, but isn’t willing to do much, if anything, to earn them. Democrats suffer from a prepositional disconnect: Harris and her surrogates talk at men, not to or, better still, with them.
If she loses to Trump, a major contributing factor will be the perception that Harris and the Democrats don’t like men.
This is puzzling. Harris knows men. She’s married to one. Most of her Senate colleges are men. Her running mate is a guy, albeit a goofy beta. Why can’t Kamala speak fluent dude?
A more talented politician would recognize male voters—especially white male voters—less as an obstacle to fool, bully or circumnavigate than as what they realty are: virgin electoral territory.
American men are suffering from a set of very real, very serious problems with which neither political party has begun to identify, much less engage.
One of Trump’s superpowers in 2016 was his recognition of the pain, frustration and anger of Rust Belt voters (including men) left behind by deindustrialization to wallow in poverty, addiction and dysfunction. Trump, and now his running mate J.D. Vance, described the shuttered factories and the blighted neighborhoods in places like Dayton, Ohio, where I grew up. They argued that American citizens deserved better and promised to fix it. Trump didn’t fix it as president. Maybe he couldn’t.
But he did see the people of Flyover Country. That was enough to take over the GOP, defeat Hillary Clinton and build the MAGA movement.
Today, boys and men represent an even bigger untapped reservoir of political support for the politician and party with enough vision to recognize it. Males are in crisis. They are angry and confused.
Men are in crisis.
They are desperate for compassion and looking for leadership.
Males are far more likely to abuse and become addicted to illegal drugs than females. Boys drop out of high school more than girls. Males are 50% of the population yet account for most fatal cancer and nearly 80% of suicides. Trapped in an increasingly feminized system of primary, secondary and higher education with rules designed for “calmer” females, boys and men are now being taught that they are historically responsible for rape, colonialism, imperialism and every other conceivable form of oppression. They are ordered to sit silently by as they are passed over for jobs, awards and other opportunities in order to make up for the historic sins of systemic sexism and misogyny. Men cannot and should not be proud of masculinity or maleness.
They ought be ashamed. As a liberal pundit put it in 2019, “Old White Men Like Me Need to Shut Up and Step Aside.”
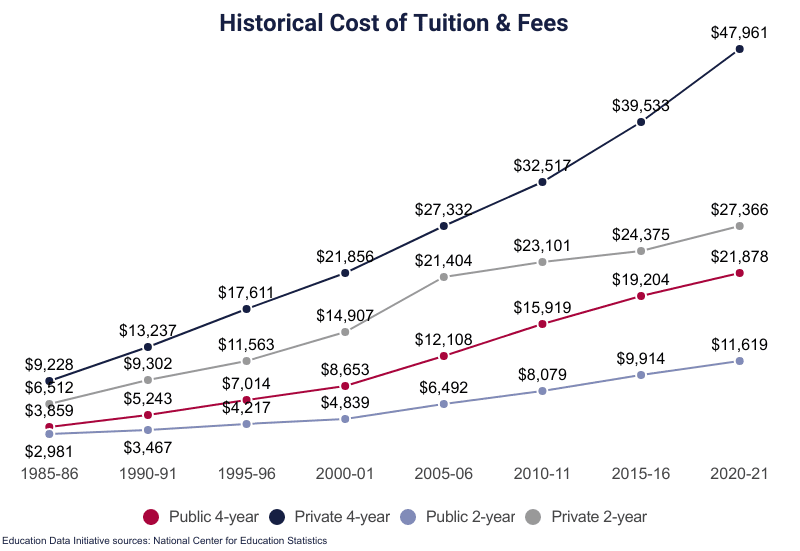
The Male Problem blows up during adulthood. 58% of college students are women; 42% are men. Moreover, women graduate in higher numbers—68% compared to 61% for guys—so the proportion of women with college degrees in the workforce is even higher. This is not a new problem; colleges began admitting more girls than boys in 1979. Nor is it a correction. Flipping a historical injustice, sexual discrimination, on its head does not redress it; it merely reverses the role of victim and oppressor.
Cultural progressives posit an identitarian version of trickle-down economics in which equity erases the old gender pay gap that favored men, lifting up women without hurting men. But wages are a zero-sum game that men are losing. “In 1979, the median hourly wage for women was 62.7% of the median hourly wage for men; by 2012, it was 82.8%,” according to the left-leaning Economic Policy Institute. “However, a big chunk of that improvement—more than a quarter of it—happened because of men’s wage losses, rather than women’s wage gains.”
Gender inequality increasingly looks like a two-way street, with males bearing the brunt not only economically but socially because high-earning women are not willing to marry, support or subsidize lower-achieving men. Trophy husbands, cultural shifts notwithstanding, are not a thing.
It’s hardly surprising that the unabashedly macho swagger of Trumpism finds a receptive audience among America’s lost boys. As the conservative activist Charlie Kirk told Vanity Fair, guys “want to be part of a political movement that doesn’t hate them.”
That’s not the Democrats.
(Ted Rall (Twitter: @tedrall), the political cartoonist, columnist and graphic novelist, co-hosts the left-vs-right DMZ America podcast with fellow cartoonist Scott Stantis. His latest book, brand-new right now, is the graphic novel 2024: Revisited.)

 “Get a job!” That’s the clichéd response to panhandlers and anyone else who complains of being broke. But what if you can’t?
“Get a job!” That’s the clichéd response to panhandlers and anyone else who complains of being broke. But what if you can’t? Serendipity plays such a starring role in our lives that we never stop to ask ourselves whether we ought to accept it. A random event, especially one that turns out to be your “big break,” becomes a charming story—even though, really, such happenstance is an indictment of a system that is no system at all.
Serendipity plays such a starring role in our lives that we never stop to ask ourselves whether we ought to accept it. A random event, especially one that turns out to be your “big break,” becomes a charming story—even though, really, such happenstance is an indictment of a system that is no system at all.