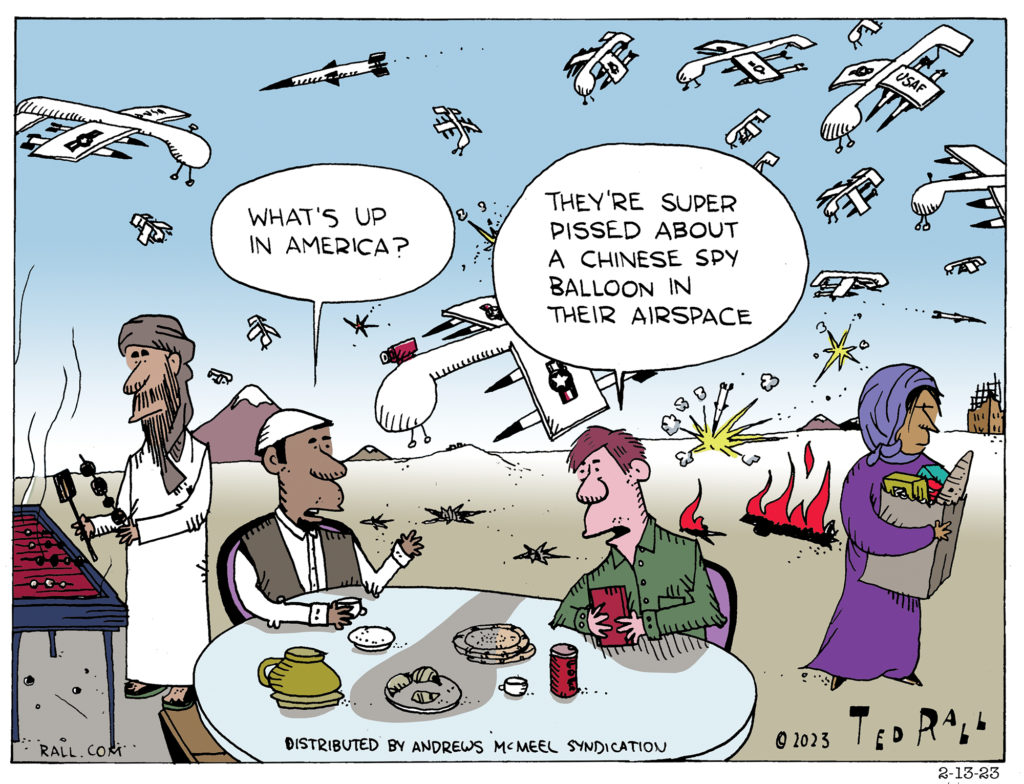
No country in the world invades the sovereign airspace of other nations as brazenly or extremely as the United States with spy drones, assassination drones, spy satellites and outright invasions. So it’s beyond rich to see U.S. officials whine so much about China’s survelliance balloon.
Just a Little More War Please
As we saw in Vietnam and elsewhere, what begins as relatively minor involvement in a proxy conflict overseas can gradually evolve into full-fledged warfare that costs billions of dollars and thousands of lives as the sunk-cost fallacy takes over. We can’t give up now. We’ve already invested too much.
DMZ America Podcast 69: Could Ukraine War Go Nuclear? Are Saudis Fixing the Midterms? How Bad Is Afghanistan?
Editorial cartoonists and best friends Scott Stantis (Right) and Ted Rall (Left) discuss the week’s news for their DMZ America podcast, where disagreement and civility go hand in hand. First, Washington floats the idea that Russia might use tactical nuclear weapons and suggests the US might escalate to a “hot” war with Russia. Second, Scott offers a unified theory explaining why Saudi Arabia and OPEC denied Biden’s pleas for increased oil production and how this might be an October Surprise. Finally, Afghanistan has collapsed again. Here’s why you should care.
4 Lessons from Afghanistan
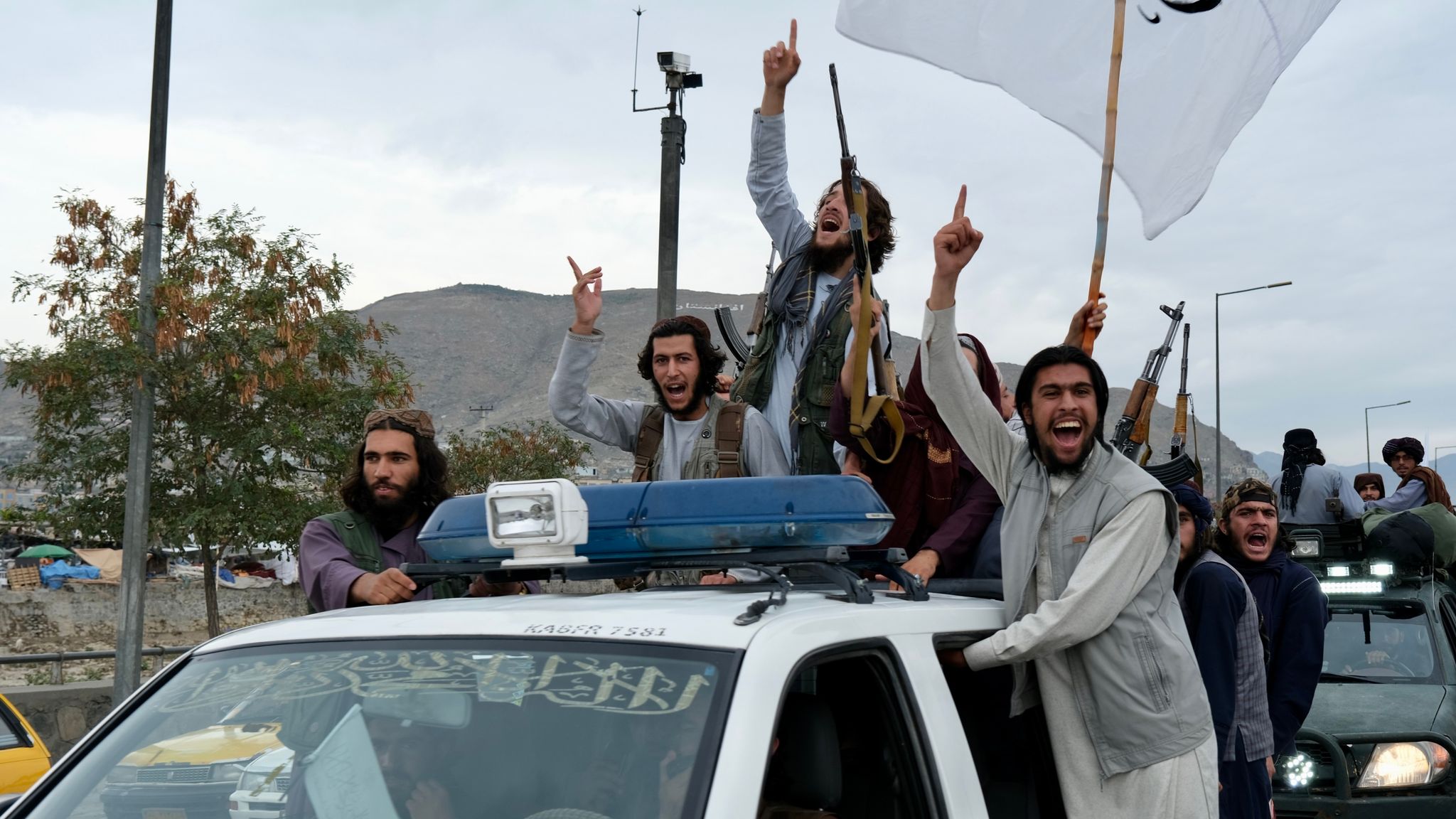

One year ago, America lost yet another war. Afghanistan is right back where it was two decades ago, under control of the Taliban. The question is: what, if anything, have we learned?
Make any mistake you like, but don’t make the same mistake twice—or four times. The U.S. committed the same errors of omission and commission in Vietnam, and then Iraq; our failure to draw intelligent conclusions from those conflicts and apply them going forward led us to squander thousands of more lives and billions of more dollars in Afghanistan. Here we go again: unless we learn from our decision to go to war against Afghanistan and then occupy it, we are doomed to our next debacle.
Afghanistan Lesson #1: When politicians tell you that war is necessary and justified, always be skeptical.
President George W. Bush told us that we had to invade Afghanistan in order to bring Osama bin Laden to justice for 9/11. Almost certainly false; the guy was probably in Pakistan. And if bin Laden was in Afghanistan, Bush could have instead accepted the Taliban’s repeated offers to extradite the accused terrorist. Bush argued the war was necessary to take out four training camps allegedly used by Al Qaeda. But Bill Clinton bombed six such camps using cruise missiles in 1998, no war required.
Bush’s casus belli for Afghanistan made no more sense than his evidence-free weapons of mass destruction in Iraq or the fictional Tonkin Gulf incident LBJ used to get us into Vietnam. It’s long overdue for American voters to download and install a sturdy BS detector about wars, particularly those on the other side of the planet.
Lesson #2: Never install a puppet government.
Of the countless mistakes the U.S. made in Vietnam, no single screwup led to more contempt for the United States than its sustained support for the deeply unpopular, brutal, autocratic president of South Vietnam, Ngo Dinh Diem. Saddam Hussein looked positively brilliant in comparison to the exiled con man, Ahmed Chalabi, whom Bush tried to replace him with. Rather than allow Afghans at the post-invasion loya jirga council meeting to choose their own ruler, like the long-exiled king, the U.S. pulled strings behind the scenes by buying the votes of corrupt warlords in support of the dapper Hamid Karzai, who had little popular support. Three years later, even the establishment New Yorker conceded that “if American troops weren’t there, Karzai almost certainly wouldn’t be, either.”
The U.S. propped up Karzai and his successor and close ally Ashraf Ghani for 17 more years.
Lesson #3: Never try to exclude an entire political party or group from a nation’s political life.
The Taliban’s base of power was the ethnic Pashtuns who comprised 40% of Afghanistan’s population. Yet the Taliban were not permitted to attend the loya jirga. They could not run in parliamentary elections under the U.S.-backed puppet government. Marginalized and “alienated from the central government, which they believe[d was] unfairly influenced by non-Pashtun leaders and interests,” in the words of a prescient 2009 Carnegie Endowment white paper, they had two options: stand down and shut up, or resort to guerilla warfare.
The U.S. messed up the same way in Vietnam and Iraq. In U.S.-backed South Vietnam, communists and their nationalist allies were excluded from electoral politics. Iraq’s Sunnis, 32% of the nation, lost their leader when Saddam was overthrown by U.S. forces, got fired from the military and other jobs by Bush’s idiotic deBaathification policy and humiliated by America’s new darlings, Shia politicians and their factions—sparking a bloody civil war and leading to U.S. defeat.
Lesson #4: Never be a sore loser.
European powers that offered financial assistance and training to their former colonies after independence in places like Africa continued to enjoy influence within those countries. Examples include the UK’s relationship with India and France’s role in Mali, Senegal, the Central African Republic and even Algeria, which cast off the French yoke after an eight-year-long struggle famously characterized by torture and terrorism.
The United States should try something similar when it loses its wars of aggression: lick its wounds, acknowledge its mistakes and offer to help clean up the messes it makes when it withdraws from a country strewn with mines and cluster bombs.
It took 20 years before the U.S. reengaged with Vietnam after the fall of Saigon—two decades of squandered rapprochement and lost international trade. This occurred despite the precedent of World War II, in which U.S. occupation authorities worked to insinuate themselves with their defeated enemies Germany and Japan almost on day one, two relationships that paid off for all concerned.
Its nose bloodied by its debacle in Iraq, the U.S. has allowed Iran to become the dominant outside power inside the country.
And now the U.S. is doing the same thing in Afghanistan as in Iraq—nothing. Afghans are gaunt and hungry because of drought and the U.S. decision to cut off aid and frozen Afghan government funds. The economy is collapsing. The enormous U.S. embassy in Kabul is closed, making it impossible for Afghans to contact the U.S. government.
All that investment of money and time, and who will get the more than $1 trillion in untapped natural resources, including copper, lithium, and rare-earth elements? China, most likely. If the U.S. could get over itself, it might salvage some influence over the new Taliban government in Kabul and open new markets. Let girls go to school and women work, President Biden could tell them, and we’ll release some funds. Arrest and hand over figures like the recently droned Ayman al-Zawahiri, who was living in Kabul, and we’ll restore aid. Carry out more reforms and we’ll establish diplomatic ties.
Picking up your toys and going back to your house after losing a fight might feel good. But it’s immature and counterproductive in a world in which success depends on having friends and collaborators.
(Ted Rall (Twitter: @tedrall), the political cartoonist, columnist and graphic novelist, co-hosts the left-vs-right DMZ America podcast with fellow cartoonist Scott Stantis. You can support Ted’s hard-hitting political cartoons and columns and see his work first by sponsoring his work on Patreon.)
First They Came for the Foreigners’ Bank Accounts

Adam Smith wrote that the efficiency of markets relies on the free movement of goods. What happens when governments seize property in order to exert political pressure—or out of greed?
A major, arguably the primary, incentive of the capitalist system is that it offers the potential of accruing wealth. Individuals and companies rely on government to maintain order, keep conditions like interest rates stable and protect accumulated assets from bank failures, devaluation, fraud and theft, without regard for the political orientation of their owner. In recent years, however, the United States has increasingly been putting its thumb on the scale for ideological reasons, taking assets by ethically and legally dubious means, and imperiling its reputation as a safe haven for deposits and investments.
From the 62-years-and-counting trade embargo against Cuba to the severing of ties with Iran following the hostage crisis to the isolation of South Africa to punish apartheid, the U.S. has repeatedly turned to economic sanctions in the postwar era. The outright seizure of foreign assets held in the U.S. has increasingly become a part of the mix of pressure tactics.
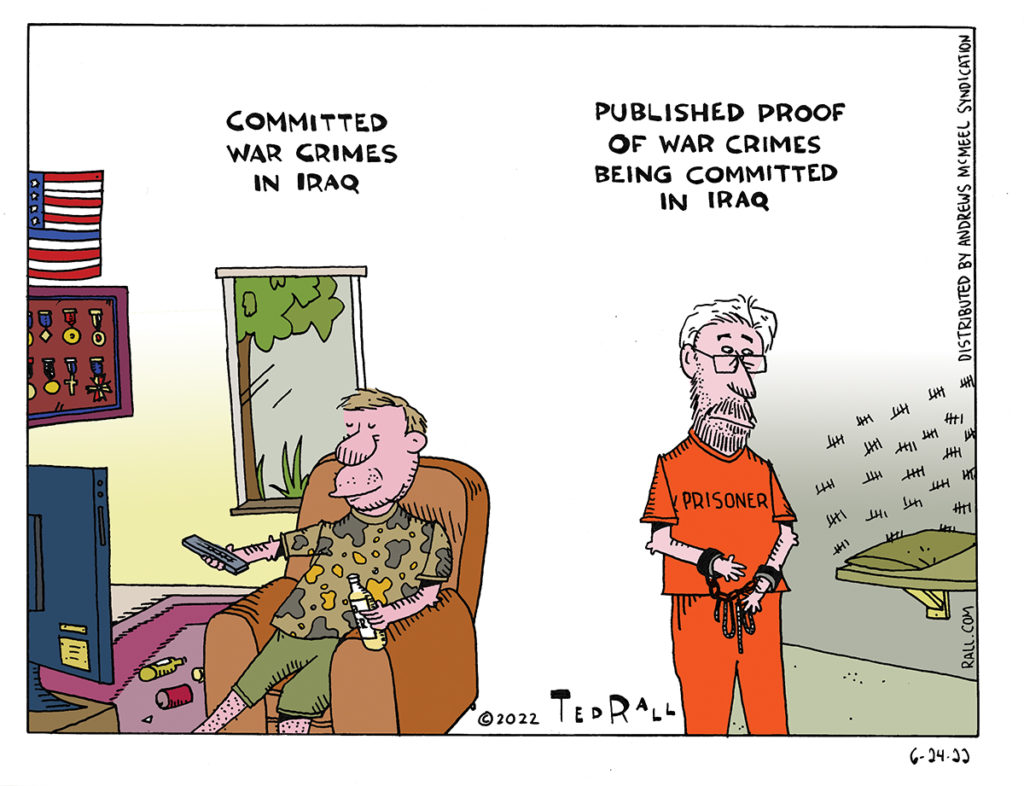
President George W. Bush took $1.7 billion from Iraq’s foreign reserves in 2003 and transferred an additional $600 million to a slush fund to finance anti-Saddam Hussein factions.
Shortly before the 2011 overthrow and killing of dictator Moammar Ghaddafi, President Barack Obama ordered that U.S. banks freeze $30 billion held by the Central Bank of Libya and the Libya Investment Authority, a sovereign wealth fund, and use some of the money to fund Benghazi-based anti-Ghaddafi rebel groups, some of which morphed into radical jihadi terrorist organizations.
Obama signed a 2012 law allowing frozen Iranian assets to be made available to settle claims by families of Hezbollah victims in Lebanon. “It is theft … it is like stealing Iran’s money and we condemn it,” an Iranian spokesman said.
Refusing to accept the legitimacy of the country’s sitting president, President Donald Trump attempted a backdoor economic coup in Venezuela with a 2019 order granting opposition leader Juan Guaidó—even though he wasn’t a government official—authorization to dispose of assets and property in U.S. bank accounts under the name of the government of Venezuela.
The Biden Administration recently grabbed $7 billion in deposits at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York in the name of the central bank of Afghanistan, Da Afghanistan Bank. The Taliban, who seized power in late August, claim they are the new government and that the money should be sent to them so they can, among other things, address mass starvation resulting from the post-U.S.-withdrawal economic collapse. The U.S., however, refuses to recognize the Taliban (or the former regime led by Ashraf Ghani) as the government of Afghanistan.
In February President Biden signed an executive order transferring $3.5 billion to a trust fund that may be used to settle civil claims by the families of 9/11 victims and the remaining $3.5 billion to a second fund that might eventually be drawn down upon by humanitarian aid organizations. China’s reaction received widespread, approving news coverage. “This is flagrant robbery and shameless moral decline. The U.S. should immediately return the stolen money back to the Afghan people, and compensate people in Afghanistan, Iraq, Libya and more who died or suffered losses from the U.S. military invasions,” said Foreign Ministry spokesperson Hua Chunying.
As part of its sanctions against Russia to punish it for invading Ukraine, the U.S. has frozen $100 billion in Russian foreign-exchange reserves held at the Fed and moved to seize superyachts, luxury apartments and bank accounts held by oligarchs close to Russian President Vladimir Putin. Representative Tom Malinowski (D-NJ), co-sponsor of a House resolution urging the sale of frozen Russian assets to benefit Ukraine that passed by an overwhelming majority, said that Russia should never get them back: “Can we imagine giving all of Russia’s wealth — the yachts, the bank accounts, the villas, the planes — back to Putin and his cronies as Ukraine lies in ruin, as the Ukrainians bury their dead? We cannot imagine doing that. We will not do that.”
Russia, however, has long anticipated American sanctions and has engaged in a policy of “de-dollarization” of its foreign currency reserves to soften the blow. “Crucially, the once-dominant dollar now accounts for only 16% of Russia’s currency reserves, which Moscow has replaced with euros, China’s renminbi, and gold,” reports The New York Times.
Other countries with less than perfect relationships with the United States are searching for ways to keep their assets out of our clutches. Brazil and India are worried about being targeted over their environmental policies. Do we really want to solidify our reputation as a place where your bank account and even your home can be taken by the U.S. government because you are friends with the president of your country at a time when the U.S. and your country aren’t getting along?
Kleptomaniacal economic warfare has also become pervasive within our borders. Police agencies routinely use civil asset forfeiture to take the cars, houses, boats, cash and other property of people they suspect of involvement with crime or illegal activity. More than $68 billion worth of personal property has been seized by cops over the last 20 years within the United States, all without due process. Incredibly, property is not returned even when no charges are filed or a trial ends with a not-guilty verdict.
We may not have much sympathy for Russian oligarchs or people whose flashy lifestyles attract the wrong kind of attention from the police. But it’s not hard to imagine a not-distant future when the government might seize an average law-abiding citizen’s middle-class house because they espouse the wrong politics. The way things are going, we may soon see an ill-considered tweet lead to someone’s bank account being frozen and the assets redirected to some bureaucrat’s favorite cause.
(Ted Rall (Twitter: @tedrall), the political cartoonist, columnist and graphic novelist, is the author of a new graphic novel about a journalist gone bad, “The Stringer.” Order one today. You can support Ted’s hard-hitting political cartoons and columns and see his work first by sponsoring his work on Patreon.)
Biden is Giving $40 Billion to Ukraine. Here’s What That Money Could Do Here.

On top of the $2 billion it already sent to Ukraine, the Joe Biden Administration has asked Congress to ignore its previous request for a $10 billion to pay for updated COVID-19 vaccines for American citizens (pandemic? what pandemic?) and send an additional $33 billion to Ukraine instead. The House of Representatives not only obliged, but authorized more than Biden wanted, $40 billion.
The U.S. Congress does this with military spending all the time. They live to please!
Every Democratic congressman voted “yes” to send weapons to a country that has “several hundred monuments, statues, and streets named after Nazi collaborators,” according to The Forward. That even includes AOC’s “Squad,” who claimed to be progressive.
In the Senate, a rare voice of opposition was raised by libertarian Republican Rand Paul. “We don’t need to be the sugar daddy and the policemen of the world,” Paul remarked. For his trouble, Paul was bizarrely accused of “treason” by online commenters who suggested that his surly Kentucky neighbor should assault him again. All Paul wanted was a week to go over exactly where all that money is going.
Whatever you think of the crisis in Ukraine, Paul has a point. A week isn’t going to make any difference. We should distrust bullies who tell us there’s no time to think, hurry up, shut up, do what we tell you. The total lack of debate in Washington, and in the news media, over the quick transfer of $40 billion to a country that is not a U.S. ally, has a grim human rights record and recently banned a bunch of political parties and opposition cable news channels, ought to prompt some sort of discussion. First and foremost, we ought to consider just how much money $40 billion is and what it could do here in the United States, for Americans.
The $40 billion we are sending to Ukraine will not change the outcome of the war. The United States would never commit enough money or ground troops to do that because it would risk World War III with Russia. The $40 billion will buy a lot of weapons and ammunition that will kill Russians and Ukrainians—nothing more, nothing less.
So how much, exactly, is $40 billion?
Here in the United States, here are some of the things that $40 billion could do:
A $2,000 scholarship for every college student.
A $6,000 scholarship for every college student who is officially in poverty.
$72,000 to every homeless person.
$2,400 to every veteran.
$410,000 to every public school.
$1.3 million to every public high school. It could be used to buy books and other equipment, fix broken infrastructure, build something new for the kids. $1.3 million would pay the salaries of 20 new teachers for 10 years.
$500 to each American family. I pledge to use my $500 not to kill any Russians or Ukrainians.
$420 to every cat. That’s a lot of kibble and litter. Cats don’t kill Russians or Ukrainians.
$2 million each to every person wrongfully convicted of a murder they didn’t commit.
Give a new, fully-loaded car to a million people.
Give a sweet, fully-loaded Macbook Pro laptop to 10 million people.
Give a sweet new TV to 100 million people.
Everyone who currently subscribes to Netflix gets three years for free.
Every adult gets a free subscription to the Washington Post digital edition for three years.
Every adult gets 15 free tickets to the actual, real, in-person, not-at-home movies.
$40 billion would repair almost all of the 220,000 bridges in the United States that need to be repaired and replace all of the 79,500 that need to be replaced. Add the $2 billion we already sent to Ukraine and you can delete the word “almost.”
$40 billion would buy Twitter.
$86,000 for everyone raped over the last year.
$7,000 to help the caregivers of everyone suffering from dementia.
It would hire 50,000 journalists for 20 years. There are only 6,500 now.
$4,000 to every self-identified Native American and Alaska Native. It’s not nearly enough considering what has been done to them, but it’s better than the current nothing.
What if, for some strange reason, we don’t want to use that $40 billion to help our own people right here at home, one out of nine of whom is officially poor—some of whom are actually starving? While the inclination to shovel money at other countries while so many of our own citizens are suffering is nearly impossible to understand, some people (the President, several hundred members of Congress) have such a mindset and therefore must be addressed.
If we’re looking for a country in dire need of, and richly deserving of, $40 billion, we need look no further than Afghanistan.
Afghanistan, which the U.S. brutally occupied for 20 years after invading without just cause, is suffering from the biggest humanitarian crisis in the world. Half its population—20 million people—is suffering from “acute hunger,” according to the UN. The nation collapsed because the U.S. pulled the plug on the economy when it withdrew, imposed draconian economic sanctions in a fit of spiteful pique and seized $7 billion in Afghanistan government funds. Biden has promised a little aid, though none has shown up in Kabul.
From the Intercept: “A senior Democratic foreign policy aide, who was granted anonymity to openly share his thoughts on the Biden administration’s actions, said the policy ‘effectively amounts to mass murder.’ According to the aide, Biden ‘has had warnings from the UN Secretary General, the International Rescue Committee, and the Red Cross, with a unanimous consensus that the liquidity of the central bank is of paramount importance, and no amount of aid can compensate for the destruction of Afghanistan’s financial system and the whole macro economy.’”
Democrats recently joined Republicans to vote no on a modest proposal to study the effect of U.S. sanctions against the Afghan people.
Then again, we really do need that COVID money.
(Ted Rall (Twitter: @tedrall), the political cartoonist, columnist and graphic novelist, is the author of a new graphic novel about a journalist gone bad, “The Stringer.” Order one today. You can support Ted’s hard-hitting political cartoons and columns and see his work first by sponsoring his work on Patreon.)
How the U.S. Lost the Ukraine War

The effect of Western sanctions may cause historians of the future to look upon the conflict in Ukraine as a net defeat for Russia. In terms of the military struggle itself, however, Russia is winning.
Watching American and European news coverage, you might ask yourself how can that be? It comes down to war aims. Russia has them. They are achievable.
The United States doesn’t have any.
“As the war in Ukraine grinds through its third month,” the Washington Post reports, “the Biden administration has tried to maintain a set of public objectives that adapt to changes on the battlefield and stress NATO unity, while making it clear that Russia will lose, even as Ukraine decides what constitutes winning. But the contours of a Russian loss remain as murky as a Ukrainian victory.”
War aims are a list of what one side in a military conflict hopes to achieve at its conclusion.
There are two kinds.
The first type of war aim is propaganda for public consumption. An overt war aim can be vague, as when President Woodrow Wilson urged Americans to enter World War I in order to “make the world safe for democracy” (whatever that meant) or specific, like FDR’s demand for the “unconditional surrender” of the Axis powers. A specific, easily measured, metric is better.
Covert war aims are goals that political and military leaders are really after. A covert war aim must be realistic. For example, contrary to the long-standing belief that he viewed the outbreak of the Korean war as an irritating distraction, Stalin approved of and supported North Korea’s invasion of the South in 1950. He didn’t care if North Korea captured territory. He wanted to drag the United States into a conflict that would diminish its standing in Asia and distract it from the Cold War in Europe. The Soviet ruler died knowing that, whatever the final outcome, he had won.
A publicly-stated war aim tries to galvanize domestic support, which is especially necessary when fighting a proxy war (Ukraine) or war of choice (Iraq). But you can’t win a war when your military and political leaders are unable to define, even to themselves behind closed doors, what winning looks like.
America’s biggest military debacles occurred after primary objectives metastasized. In Vietnam both the publicly-stated and actual primary war aim was initially to prevent the attempted overthrow of the government of South Vietnam and to prevent the spread of socialism, the so-called Domino Theory. Then the U.S. wanted to make sure that soldiers who had died at the beginning of the war hadn’t died in vain. By the end, the war was about leveraging the safe return of POWs. A recurring theme of accounts by soldiers in the jungle as well as top strategists at the Pentagon is that, before long, no one knew why we were over there.
Again, in Afghanistan after 2002, war aims kept changing. Mission creep expanded from the goal of defeating Al Qaeda to apprehending Osama bin Laden to building infrastructure to establishing democracy to improving security to using the country as a base for airstrikes against neighboring Pakistan. By 2009 the Pentagon couldn’t articulate what it was trying to accomplish. In the end, the U.S. did nothing but stave off the inevitable defeat and collapse of its unpopular Afghan puppet regime.
Clear war aims are essential to winning. Reacting to his experience in Vietnam, the late General Colin Powell led U.S. forces to victory in the first Gulf War with his doctrine that a successful military action enjoys strong domestic political support, is fought by a sufficient number of troops and begins with a clear military and political objective that leads to a quick exit. After Saddam Hussein’s forces were routed from Kuwait, George H.W. Bush ignored advisers who wanted to expand the conflict into Iraq. America’s mission accomplished, there was a tickertape parade down Broadway, the end.
The U.S. too often involves itself in foreign conflicts without declaring clear war aims—or even knowing themselves what they are. In Korea, Vietnam, Afghanistan and Iraq, unclear or shifting war aims led to endless escalation followed by fatigue on the home front, declining popular will and defeat. Our involvement in the proxy conflicts in Yemen and Syria also have the character of forever wars, though American voters won’t pay much attention as long as the cost is limited to taxpayer dollars rather than their sons and daughters.
I wrote a piece in 2001 titled “How We Lost Afghanistan.” Given that the U.S. had just overthrown the Taliban, it was cheekily counterintuitive. But I was looking at the Afghan war from the Afghan perspective, which is why I was right and the mainstream media was wrong. I see a similar situation unfolding in Ukraine. We are so misled by our cultural biases that we fail to understand the Russian point of view. The U.S. failure to articulate war aims stems from arrogance. We think we’re so rich and powerful that we can beat anyone, even if our strategy is half-assed and we don’t understand politics on the other side of the planet, where the war is.
President Joe Biden’s approach to Ukraine appears to boil down to: let’s throw more money and weapons into this conflict and hope it helps.
That’s not a strategy. It’s a prayer.
Biden says he wants to preserve Ukraine as a sovereign state and defend its territory. But how much territory? How much sovereignty? Would Biden accept continued autonomy for the breakaway republics in the Dombas? The White House appears unwilling to escalate by supporting an attempt to expel Russian forces from eastern Ukraine, much less Crimea—where they are welcomed by a population dominated by ethnic Russians. Short of a willingness to risk nuclear war, the likely ultimate outcome of the U.S. position will be a Korea-like partition into western and eastern zones. A divided Ukraine would create a disputed border—which would disqualify a rump Ukrainian application to join NATO.
Russia’s primary demand is that Ukraine not join NATO. If America’s goal winds up resolving the main reason President Vladimir Putin invaded Ukraine, why is the U.S. involved? A war aim that neatly aligns with one’s adversary’s is grounds for peace talks, not fighting.
Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin recently added a second Ukraine war aim: “We want to see Russia weakened to the degree that it can’t do the kinds of things that it has done in invading Ukraine.” Weakened to what extent? Reduced to a failed state? Mildly inconvenienced? Not only is the policy dangerous, it fails to define a clear objective.
Russia, on the other hand, has secured its allies in the autonomous republics and created a buffer zone to protect them. Crimea will remain annexed to Russia. NATO membership for Ukraine, a chimera to begin with, is now a mere fever dream. Unlike the U.S., the Russians declared their objectives and achieved the important ones.
(Ted Rall (Twitter: @tedrall), the political cartoonist, columnist and graphic novelist, is the author of a new graphic novel about a journalist gone bad, “The Stringer.” Order one today. You can support Ted’s hard-hitting political cartoons and columns and see his work first by sponsoring his work on Patreon.)
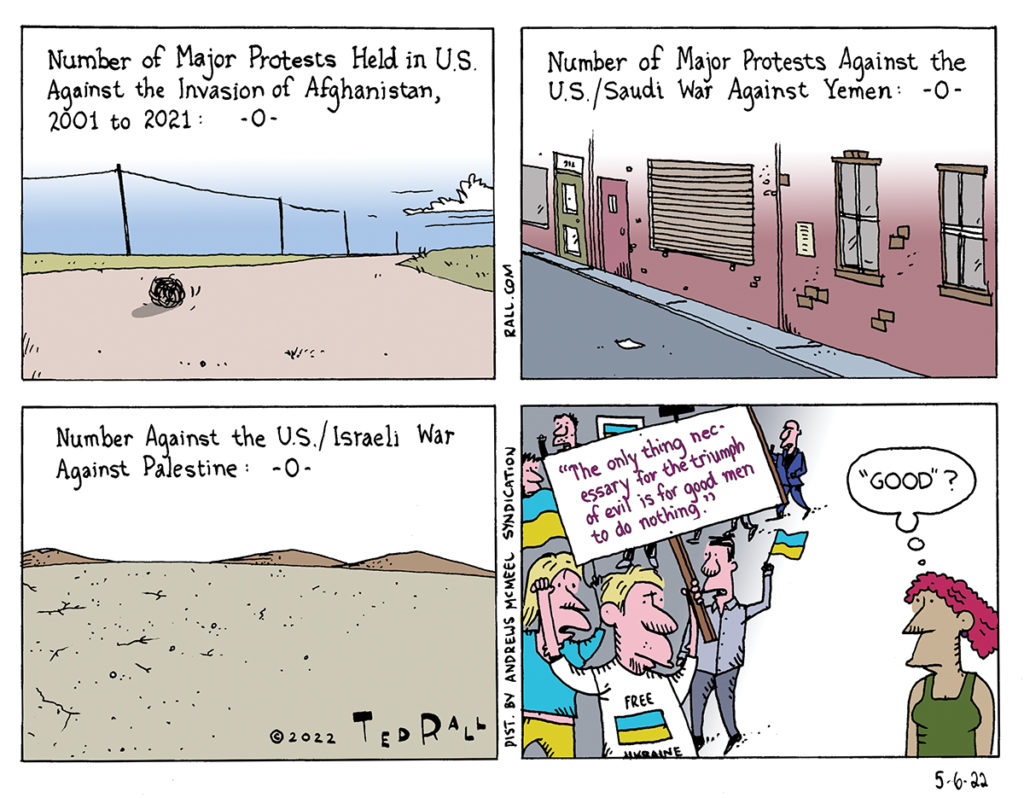
The Only Thing Necessary for Evil to Triumph
“The only thing necessary for the triumph of evil is for good men to do nothing.” That statement is often misattributed to Edmund Burke. After Russia invaded Ukraine, many Americans who didn’t have anything to say about the invasion of Afghanistan or Iraq, much less torture at Guantánamo and elsewhere, or Yemen, or Palestine, suddenly started wearing blue and yellow flags. They weren’t good before, so how can these self-serving souls think they are suddenly being good now?