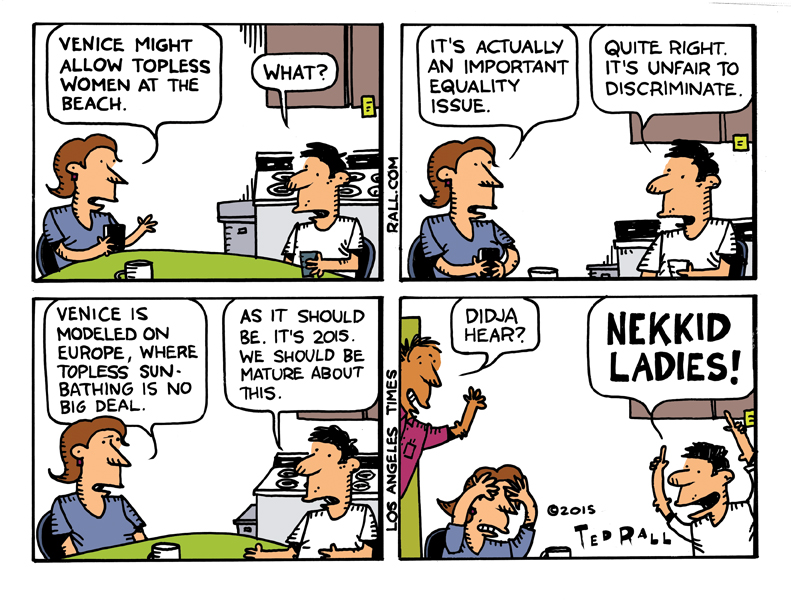
“Who had a good year?” my friend and cartoonist colleague asked me. Again. “Who’ll win?” We have the same conversation every April.
A couple of weeks ago, it was time once again for an annual ritual familiar to thousands of journalists: attempting to predict the winners of the Pulitzer Prizes.
“They’ll give it to some loser. Like they always do,” I replied. “Or they won’t, and someone good will get it. Who knows? When are you going to accept that the Pulitzers are a completely, totally random occurrence?”
This is the biggest unspoken truth about the most respected award in American mediadom: there is no rhyme or reason to who wins a Pulitzer.
Theoretically, Columbia University awards the Pulitzer to the best work done the previous year in each given category: best play, best biography, best news photography of 2014, etc.
In reality, anyone can win. Anyone can be snubbed. It’s like a tornado tearing through a neighborhood, leaving one house standing intact while the others all get their roofs ripped off. Why that one? Who knows?
Many groundbreaking, big-name cartoonists get snubbed their entire careers, yet the list of winners includes many forgotten even to geeks of the genre — who remembers Edmund Valtman and Casey Orr? One recent April, I had to Google the name of the winning cartoonist. In a profession with fewer than 30 full-timers, I’d never heard of him (nor had many of my colleagues).
To call the Pulitzers quirky would be putting it mildly. There are repeat finalists who never win the actual prize. An artist may make a big splash in a given year, creating a single piece or series of cartoons widely discussed in the media, yet get passed over, even as a finalist. When the winner is announced, whether we love the cartoonist’s work or think he or she is awful, the selection always feels like it comes out of left field — not least to the winner himself or herself. It’s like — really? Him? Me?
Disclosure: I have been a finalist once. Feel free to call it sour grapes — you wouldn’t be the first. But not every cartoonist has gotten to be a finalist, so I have little reason to complain (not that it stops me).
Truth is, I’m fascinated by systems, particularly those in which subjective human beings are assigned to decide objective truths; whether it’s guilt or innocence at trial or who drew the best cartoons over a 12-month period, I am fascinated by process (procès is the French word for trial.)
Alongside my colleagues I have studied and discussed the outcome of the Pulitzer Prize for my category (editorial cartooning) for more than 20 years. It’s an obsession, and perhaps not a good for my psyche, but there it is. Over the years, many members of the cartooning award committee, which picks the three finalists, have confided the details of their deliberations. I know how they winnow down stack of entries down to a small group of contenders, what criteria they consider, how they discuss their final choices.
So what accounts for the Prize’s wild unpredictability?
For a long time, I was convinced that the explanation for Pulitzer weirdness lay primarily with process.
You’d think every committee member would look at every entry, right? No. To make the job easier, committees some years divvy up the entries among the jurors. Let’s say there are 80 entries and four jurors. Each juror reads his 20-share of entries, then divides them into “yesses” and “nos.” The yes entries go the next round while the nos are purged. The other jurors will never see a portfolio rejected in the first round. Since the identity and the tastes of the juror who first (and second, and third) winds up with your portfolio, luck plays a big role.
Some years, the committee comes up with an ad hoc point system to winnow down the stack of entries: rank quality of drawing between 1 and 10, say, and quality of the writing between 1 and 5, and add the two together. Points are a sort of math, so they feel rational, but of course they’re inherently arbitrary.
I have disabused myself of the notion that Pulitzer committee members want to send some sort of message, as in “it’s time that a woman won,” or a young person, or a Republican (though that last one is highly unlikely, because only 7% of American journalists identify with the GOP). Everyone I’ve talked to who has sat in the room has told me that making a statement isn’t a major consideration, and I believe them. In fact, they usually don’t spend much time talking to each other.
I’ve heard some crazy stories.
The big one comes up every year: what with everyone in a hurry to make it to the open bar, judges rush through the process. If you’re a long-winded, wordy cartoonist, your stuff might not get read.
One year, I was told, all the entries by the “young” (i.e., under age 45) cartoonists were set aside because one of the judges couldn’t understand them, with the agreement that, later in the winnowing-down process, the youngsters would be revisited. Everyone forgot.
Every year, at least one of the jurors has never seen a political cartoon before, and has to have the form explained to him or her by other jurors. No one suggests that the judge recuse himself.
Where I am now — and this could change — is that the choice of jurors determines the winners. Specifically, and especially in the cartooning category, jurors have no taste.
Please understand! I am not saying this colloquially, as in, they have bad taste. That is not what I mean.
What I mean is that the Pulitzer jurors have no taste.
They don’t know anything about cartoons.
To have bad taste as a judge, one must possess knowledge about a subject. For example, were I to judge the Heisman Trophy, I would need to know a lot about football, especially about up-and-coming college players. If I had bad taste, I would, as a well-informed panelist, give the trophy to a player who didn’t deserve it. However, I don’t know anything about football. I don’t watch it or even read about it. I don’t even know the names of all the teams. I should not judge the Heisman Trophy because I am an idiot when it comes to football.
I have no taste in football. Indeed, to have bad taste in football would reflect a massive increase over my current knowledge.
Every year, an examination of the list of Pulitzer Prize jurors in the editorial cartooning category reveals a startling absence of basic knowledge, much less expertise, about editorial cartoons.
The United States has two dozen or so professional political cartoonists and perhaps an additional two dozen comics museum curators, academics and editorial cartooning historians. For reasons unknown, the Pulitzer folks carefully avoid inviting any of these people, who live and breathe comics, to judge the cartoon category.
This year, one of the jurors was a freelance tech writer who has written a handful of short bits about cartooning-related controversies but no, as far as I can find online, analysis or reviews. The committee for 2014 also included an adjunct curator of comics — perhaps the chief curator was busy — for an institution that doesn’t have, you know, an actual comics museum.
There was also a pair of executive editors. Unlike opinion editors and editorial page editors, executive editors don’t deal with actual cartoons on the job. They don’t choose cartoons, or work with a staff cartoonist. Indeed, these two executive editors work at papers that don’t have a cartoonist, and run few if any syndicated cartoons.
The committee’s chairman is the editor-in-chief — a position that doesn’t work with cartoons — for a paper, in San Antonio, that fired its cartoonist years ago, and never replaced him.
A two-time Pulitzer-winning political cartoonist did judge the Pulitzer this year — but not in the cartoon category.
Quirky!
What you have, then, are five people, chosen basically at random off the streets, asked to look at more than a thousand cartoons and decide which ones they like best.
“I like this one.”
“Funny!”
“Yeah.”
To be fair, other categories have fewer spectacularly unqualified jurors. Breaking news photography was judged by five photographers. Poetry, by two literature professors and a poetry columnist. History, by three historians.
Each committee of judges sends its three finalists up to the big Pulitzer Board who can select one winner, decide not to award the prize in that category at all, or select some random fourth winner outside of the three finalists.
If that’s not random enough for you, the eclectic group of editors, academics and journalists who comprise the Pulitzer Board decide winners of prizes in everything from best editorial writer to best biography to best play to best poet to best cartoonist.
These are not stupid people. But they’re also not experts in the subjects they’re asked to judge.
Steve Coll’s writing on the Middle East, South Asia and the war on terror is some of the best. But I’m not sure I trust him to pick the best editorial cartoon AND the best poem out of the, oh, two of each he reads of them each year. Because he’s an editorial page editor, I’d have faith in Paul Gigot to judge political cartoons, except for the fact that he’s at The Wall Street Journal, which doesn’t publish any. I love Gail Collins’ columns for The New York Times, but I’ve read her for decades — and never once has she mentioned political cartoons, which leads me to doubt she follows them attentively.
Assign random judges to carry out random judging processes and you get random outcomes. That’s my theory.
For now. It could change.
Because it’s all so incredibly weird.
To paraphrase Elvis Costello, I used to be disgusted. But hey — now I get it. They’re not ruling against me! It’s all random. Who knows? Maybe I’ll win! Or not. Whatever, it’s. All. Random.
Now I’m highly amused.


 Anyway, the latest development/fad on the trying-to-keep-Russian-hackers-out-of-your-personal-crap front is biometric identification: using your fingerprints (like on the iPhone), iris scans (like in creepy dystopian movies and at passport control at American airports) and voice recognition in lieu of a password.
Anyway, the latest development/fad on the trying-to-keep-Russian-hackers-out-of-your-personal-crap front is biometric identification: using your fingerprints (like on the iPhone), iris scans (like in creepy dystopian movies and at passport control at American airports) and voice recognition in lieu of a password.