I draw cartoons for The Los Angeles Times about issues related to California and the Southland (metro Los Angeles).
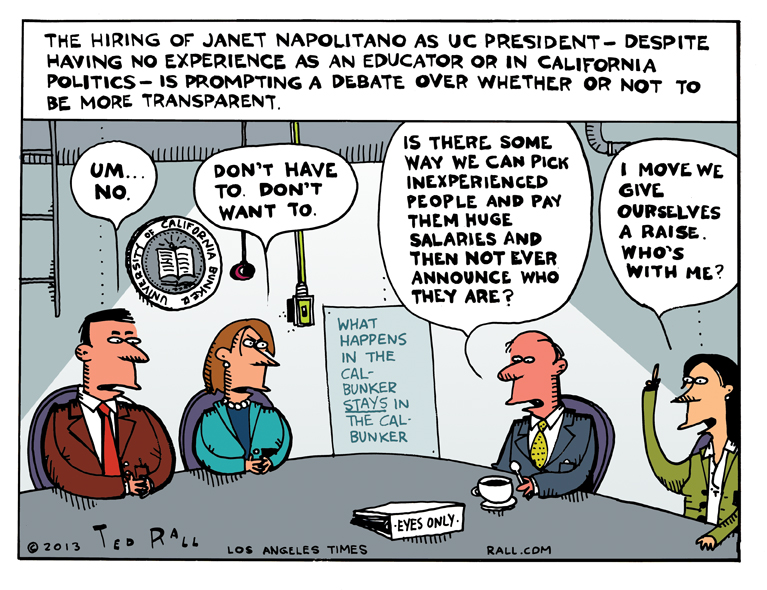
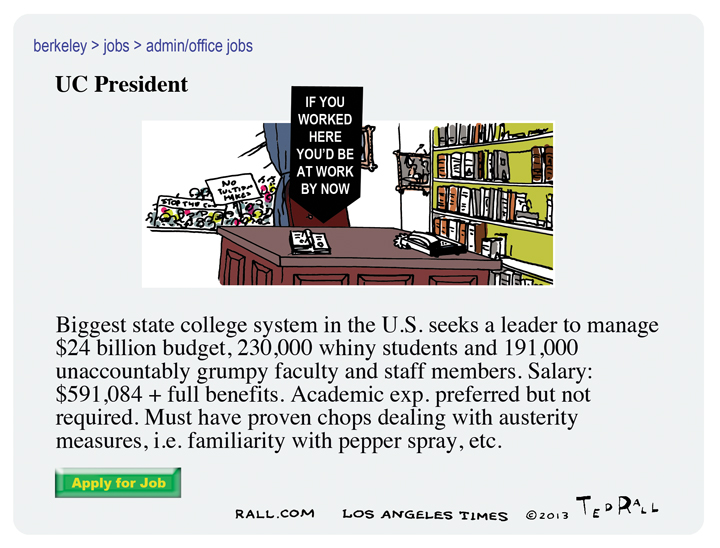
This week: The hiring of former Homeland Security Secretary Janet Napolitano as president of the University of California prompts a debate over whether or not to be more transparent.