If you suck at your job, you’ll get fired.
If you suck at your job, you’ll get fired.
If you suck because you’re lazy, you’ll definitely get fired.
Unless you’re a member of the political and economic establishment of a disintegrating superstate. If you’re incompetent and indolent but reliably loyal and unquestioning, your sinecure in the system that props up the powers that be is safe.
The New York Times, an institution so beholden to the establishment that it subjects a major presidential candidate to a media blackout and Orwellian post-publication memory-holing, is this week’s case study in establishmentarian unaccountability.
After effectively donating nearly half a billion dollars of free media coverage to the campaign of Donald Trump (or is it $1.9 billion? who can count?), corporate media is finally beginning to wonder whether teeing the country up for its first potential bona fide fascist dictatorship was a good idea.
In the Times, reliably mistaken op-ed columnist David Brooks allowed that, just maybe, opinion mongers like him ought to have noticed the building voter outrage over “free trade” deals like NAFTA and TPP — agreements supported by him and his paper’s editorial board — that gutted America’s industrial heartland and are driving the Bernie Sanders and Donald Trump campaigns. “Trump voters are a coalition of the dispossessed. They have suffered lost jobs, lost wages, lost dreams. The American system is not working for them, so naturally they are looking for something else,” Brooks wrote March 18th.
“Moreover,” continued the man who thought invading Iraq would be a cakewalk, “many in the media, especially me, did not understand how they would express their alienation. We expected Trump to fizzle because we were not socially intermingled with his supporters and did not listen carefully enough. For me, it’s a lesson that I have to change the way I do my job if I’m going to report accurately on this country.”
This is a stunning admission.
Let’s set aside the question of how likely it is that Brooks really will make the effort to get out more. (My guess: not very.) Why should the Times — and, more to the point, the readers whose paid subscriptions pay Brooks’ salary — keep a man on staff who admits that he sucks at his job because he’s too lazy to interact with the American people?
Brooks deserves to have plenty of company as he walks the unemployment version of the Long Green Mile.
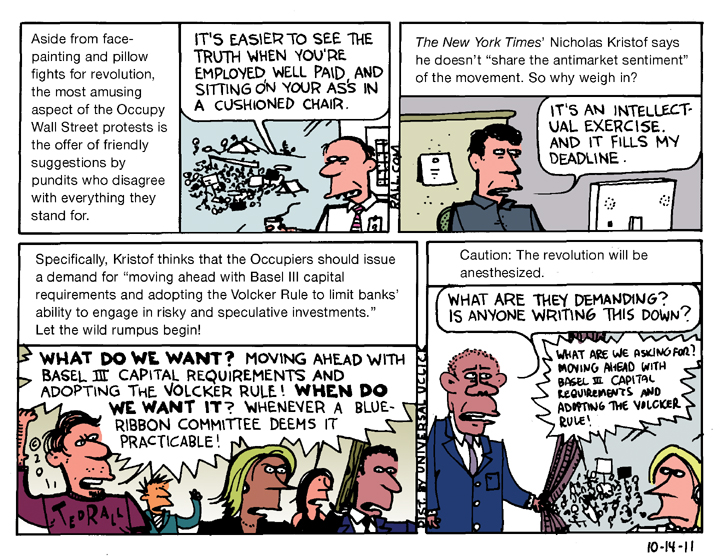
On March 28th fellow Timesman Nicholas Kristof, famous for taking young men and women to Third World nations devastated by U.S. foreign policy (though I doubt he tells them why those dumps look so dumpy), went even further, in a piece titled “My Shared Shame: The Media Helped Make Trump.”
“We were largely oblivious to the pain among working-class Americans and thus didn’t appreciate how much his message resonated,” Kristof wrote.
Most Americans are working-class. In other words, Kristof and his colleagues admit they don’t cover the problems that affect most Americans. Again: why does he still have a job?
Believe it or not, there are scores — maybe hundreds — of opinion writers who do know what’s going on in their own country. Who write well. Who get stories right. Pundits who saw the Donald Trump and Bernie Sanders populist phenomena coming. But you won’t find any of them in the print pages of major newspapers like the Times, or even in the low-pay ghettos of their web-only content.
Because you can’t be a good journalist and a shill for a corporate media obsessed with access to the powers that be.
As usual in these moments of MSM navel-gazing, they almost get it right. Kristof continues: “Media elites rightly talk wabout our insufficient racial, ethnic and gender diversity, but we also lack economic diversity. We inhabit a middle-class world and don’t adequately cover the part of America that is struggling and seething. We spend too much time talking to senators, not enough to the jobless.”
Class diversity is a real thing. Newsrooms at stodgy institutions like the Times have their token women and people of color, but most are women and POC from well-off families. They attend expensive journalism schools that don’t offer scholarships, and thus don’t produce graduates from poor families and towns. As Barack Obama and Hillary Clinton prove, coming from a traditionally disadvantaged minority group is no guarantee that someone understands or cares about the troubles of the economically oppressed.
More to the point, we need a new class of intuitive journalists. Men and women with empathy. People who have a clue about what’s happening in their own country.
(Ted Rall is the author of “Bernie,” a biography written with the cooperation of Democratic presidential candidate Bernie Sanders. “Bernie” is now on sale online and at all good bookstores.)